In our article “Can Sleep Help With Memory?,” we explore the fascinating relationship between sleep and memory. We all know that a good night’s rest is essential for various aspects of our health, but did you know that it could also enhance our memory? In this article, we delve into the surprising ways that sleep can improve our ability to remember and retain information. So, if you’re curious about boosting your memory and getting a sound sleep simultaneously, keep reading!
This image is property of www.sleephealthfoundation.org.au.
Review contents
The Importance of Sleep for Memory
Sleep is an essential aspect of our lives that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including memory. It is during sleep that our brains process and consolidate the information we have acquired throughout the day, making it easier for us to remember and retrieve that information later on. In this article, we will explore the link between sleep and memory, the different types of memory, the sleep stages involved in memory consolidation, and the various factors that can affect sleep-related memory. We will also discuss tips for improving both sleep quality and memory performance.
The Link Between Sleep and Memory
Numerous studies have highlighted the strong connection between sleep and memory. The process of memory consolidation, which involves the stabilization and strengthening of memories, occurs predominantly during sleep. This consolidation process allows us to retain and retrieve information more effectively, enhancing our overall memory capacity. Therefore, getting sufficient and quality sleep is crucial for memory retention and cognitive function.
The Role of Sleep in Memory Consolidation
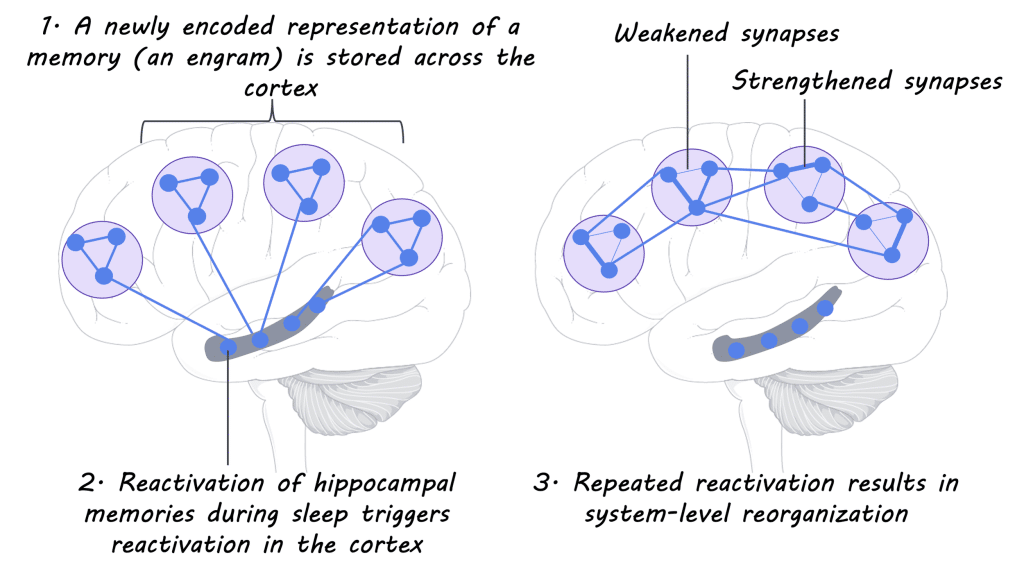
Memory consolidation refers to the process of transferring information from short-term memory to long-term memory. This process occurs during sleep, allowing our brains to solidify and integrate the new information into existing knowledge networks. While we sleep, our brains actively replay and reinforce the neuronal connections formed during waking hours, leading to the strengthening of memory traces. This consolidation process is instrumental in enhancing our ability to store and recall information effectively.
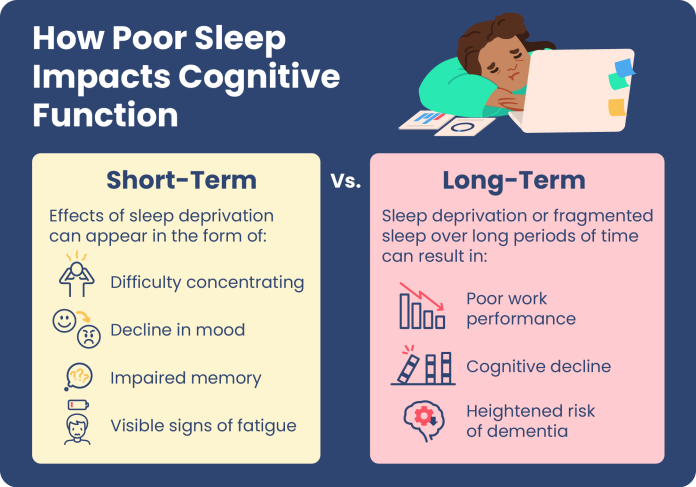
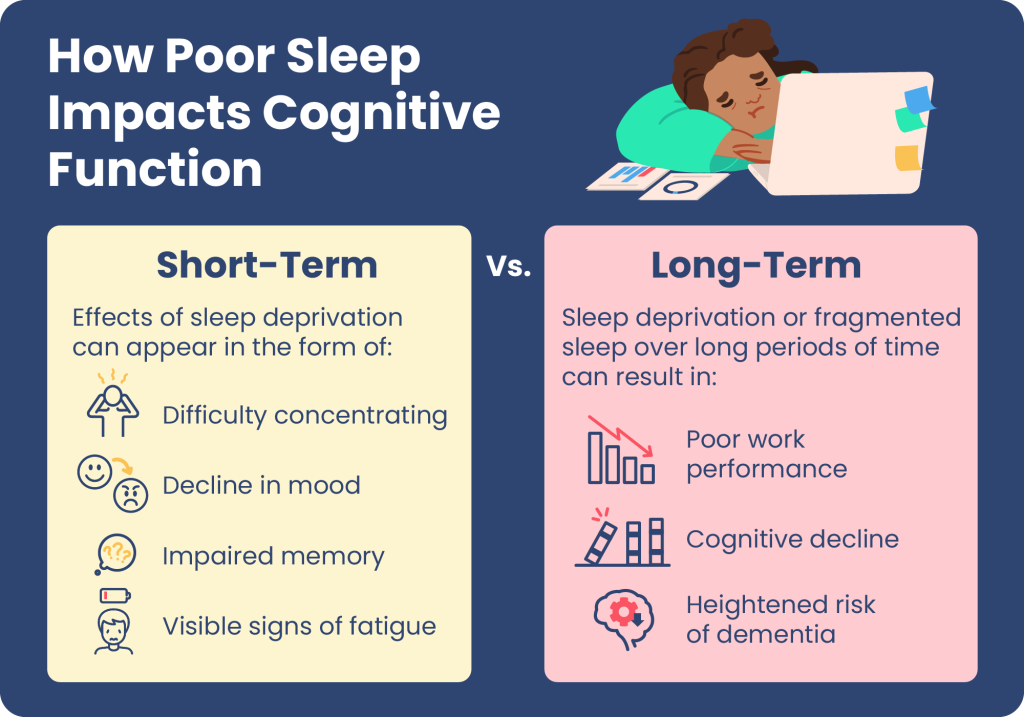
Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Memory
Sleep deprivation can have detrimental effects on memory. When we do not get enough sleep, our brains are unable to properly consolidate and store information, leading to impaired memory performance. Research has shown that even a single night of sleep deprivation can significantly impact our ability to focus, retain information, and recall memories the next day. Prolonged sleep deprivation may result in more severe memory deficits and can even contribute to the development of cognitive disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
This image is property of images.squarespace-cdn.com.
Types of Memory
To better understand the impact of sleep on memory, it is essential to familiarize ourselves with the different types of memory.
Short-Term Memory
Short-term memory, also known as working memory, is responsible for the temporary storage and manipulation of information. This type of memory allows us to hold and manipulate a limited amount of information for brief periods. It is crucial for tasks such as problem-solving, decision-making, and following instructions.
Long-Term Memory
Long-term memory is the system responsible for the storage and retrieval of information over extended periods. It can hold vast amounts of information accumulated over a lifetime. Long-term memory is further divided into explicit and implicit memory.
Explicit Memory
Explicit memory refers to the conscious recall of facts, events, and experiences. It is divided into two categories: episodic memory, which involves the recollection of specific personal events, and semantic memory, which pertains to general knowledge and concepts.
Implicit Memory
Implicit memory, on the other hand, involves the unconscious retrieval of information without conscious awareness. This type of memory is responsible for skills, habits, and conditioned responses.
Sleep Stages and Memory
Sleep is divided into two main stages: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep. Both stages play a vital role in memory consolidation.
NREM Sleep
NREM sleep consists of three stages: N1, N2, and N3. During NREM sleep, the brain enters a state of deep relaxation and restoration. N2 and N3 are particularly important for memory consolidation, as they involve slow-wave sleep (SWS). This stage is characterized by slow, synchronized brain wave activity, which is believed to facilitate the transfer of memories from short-term to long-term storage.
REM Sleep
REM sleep is a phase characterized by rapid eye movements, vivid dreaming, and heightened brain activity. During REM sleep, the brain consolidates and integrates emotional and procedural memories. This stage is crucial for memory processing, particularly for consolidating implicit memories and emotional experiences.
Non-REM and REM Sleep Cycle
Sleep occurs in cycles, with each cycle typically lasting around 90-120 minutes. These cycles alternate between NREM and REM sleep stages. As the night progresses, the duration of REM sleep increases, while the duration of deep NREM sleep gradually decreases. This cycling between NREM and REM sleep is believed to optimize memory consolidation and overall brain function.
This image is property of amerisleep.com.
The Process of Memory Consolidation
Memory consolidation involves three main processes: encoding, consolidation, and retrieval.
Encoding
Encoding is the initial process of acquiring new information and converting it into a neural representation that can be stored in the brain. It involves the activation of specific brain regions responsible for encoding various types of memory, such as the hippocampus for explicit memory and the basal ganglia for implicit memory.
Consolidation
Consolidation refers to the stabilization and strengthening of memories. It occurs primarily during sleep, as the brain replays and reinforces the neural connections formed during waking hours. This process allows the memories to become more resistant to interference and degradation and increases their accessibility for future retrieval.
Retrieval
Retrieval is the process of accessing and recalling stored information from memory. It entails the reactivation of the neural networks associated with the encoded memories. During retrieval, memories can be influenced by various factors, such as context, emotion, and the presence of cues or triggers.
Memory Improvement during Sleep
Sleep has been shown to enhance memory in several ways. Here are some of the ways in which sleep facilitates memory improvement:
Consolidation of Information
During sleep, the brain actively consolidates and integrates newly acquired information into existing knowledge networks. This consolidation process strengthens the memory traces, making the memories more stable and retrievable.
Elimination of Interference
While we sleep, the brain selectively strengthens important memories while eliminating or weakening irrelevant or interfering information. This process, known as synaptic pruning, helps declutter the memory storage and improve overall memory performance.
Strengthening of Neural Connections
Sleep plays a crucial role in the strengthening of neural connections, particularly within the hippocampus, the brain region responsible for memory formation. The reactivation of these connections during sleep enhances the synaptic strength, promoting more efficient storage and retrieval of information.
This image is property of www.sleepfoundation.org.
Sleep-Dependent Memory Benefits
Sleep has been found to enhance memory performance across various domains. Here are some specific memory benefits associated with sleep:
Motor Skill Learning
Sleep has been shown to improve motor skill learning and consolidation. During sleep, the brain replays and reinforces the neural patterns associated with the learned motor skills, leading to enhanced performance and retention of those skills.
Emotional Memory Processing
Sleep plays a vital role in processing and consolidating emotional memories. It helps regulate and integrate emotional experiences, allowing us to better understand and cope with emotional events.
Verbal Memory Enhancement
Getting sufficient sleep has been linked to better verbal memory performance. Sleep facilitates the consolidation of verbal information, making it easier to recall and utilize vocabulary, facts, and linguistic concepts.
Factors Affecting Sleep-Related Memory
Several factors can affect the relationship between sleep and memory. It is important to consider these factors to optimize sleep-related memory benefits.
Sleep Quality
The quality of sleep is crucial for memory consolidation. Disrupted or fragmented sleep, such as that experienced during sleep disorders or poor sleep hygiene, can impair memory performance. Maintaining a relaxing sleep environment and practicing good sleep hygiene can help improve sleep quality.
Sleep Duration
Both insufficient and excessive sleep can negatively impact memory. While it is important to get enough sleep for memory consolidation, oversleeping can also disrupt the sleep cycle and affect cognitive functioning. Strive for the optimal amount of sleep for your age and individual needs.
Timing of Sleep
The timing of sleep plays a role in memory consolidation. Studies have shown that a consolidation window occurs shortly after learning, during which sleep has a particularly significant impact on memory. Consequently, it is beneficial to schedule sleep shortly after acquiring new information to maximize memory retention.
This image is property of newsinhealth.nih.gov.
The Impact of Sleep Disorders on Memory
Sleep disorders can have profound effects on memory. Here are a few examples of sleep disorders and their impact on memory:
Insomnia
Insomnia, characterized by difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep, can lead to fragmented sleep and impaired memory consolidation. The fragmented nature of sleep in individuals with insomnia can disrupt memory performance, making it harder to retain and retrieve information.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea, a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, can disrupt the sleep stages necessary for memory consolidation. The repeated awakenings and drops in oxygen levels can lead to daytime sleepiness, poor concentration, and memory deficits.
Restless Legs Syndrome
Restless legs syndrome, characterized by an uncomfortable sensation and an irresistible urge to move one’s legs, can severely disrupt sleep quality. The restless legs and the resulting interruptions to sleep can impair memory consolidation and affect overall cognitive function.
Sleep-Learning Techniques
Sleep-learning techniques, also known as hypnopedia, involve the process of learning new information or skills during sleep. While the effectiveness of this approach is still a topic of debate, some techniques have shown promise in enhancing memory.
Nap-Dependent Learning
Brief naps have been found to improve memory performance by allowing for increased REM sleep, which is associated with memory consolidation. A short nap following a learning session can enhance memory retention and retrieval.
Spaced Learning
Spaced learning involves distributing learning sessions over time rather than cramming all at once. This technique takes advantage of the brain’s ability to consolidate and reinforce memories during sleep. Breaking learning sessions into shorter, spaced intervals can facilitate memory consolidation and improve overall retention.
Memory Consolidation Techniques
Certain memory consolidation techniques, such as actively rehearsing and reviewing information before sleep, have been found to enhance memory performance. Engaging in targeted memory exercises or using mnemonic techniques can help improve memory consolidation during sleep.
Practical Tips for Improving Sleep and Memory
Here are some practical tips to improve both sleep quality and memory performance:
Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Establish a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle and promote better sleep quality.
Create a Relaxing Sleep Environment
Ensure your sleep environment is conducive to relaxation and sleep. Make your bedroom dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature. Use comfortable bedding and invest in a good mattress and pillows that provide proper support.
Practice Good Sleep Hygiene
Adopt healthy sleep habits, such as avoiding caffeine and stimulating activities close to bedtime, limiting exposure to electronic devices, and engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, before sleep. Establishing a pre-sleep routine signals to your body that it is time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
In conclusion, sleep plays a vital role in memory consolidation and overall cognitive function. It is essential to prioritize sufficient and quality sleep to enhance memory performance and optimize learning. By understanding the link between sleep and memory, adopting healthy sleep habits, and addressing any sleep disorders or disturbances, we can improve both our sleep and memory capabilities, leading to a more productive and fulfilling life.