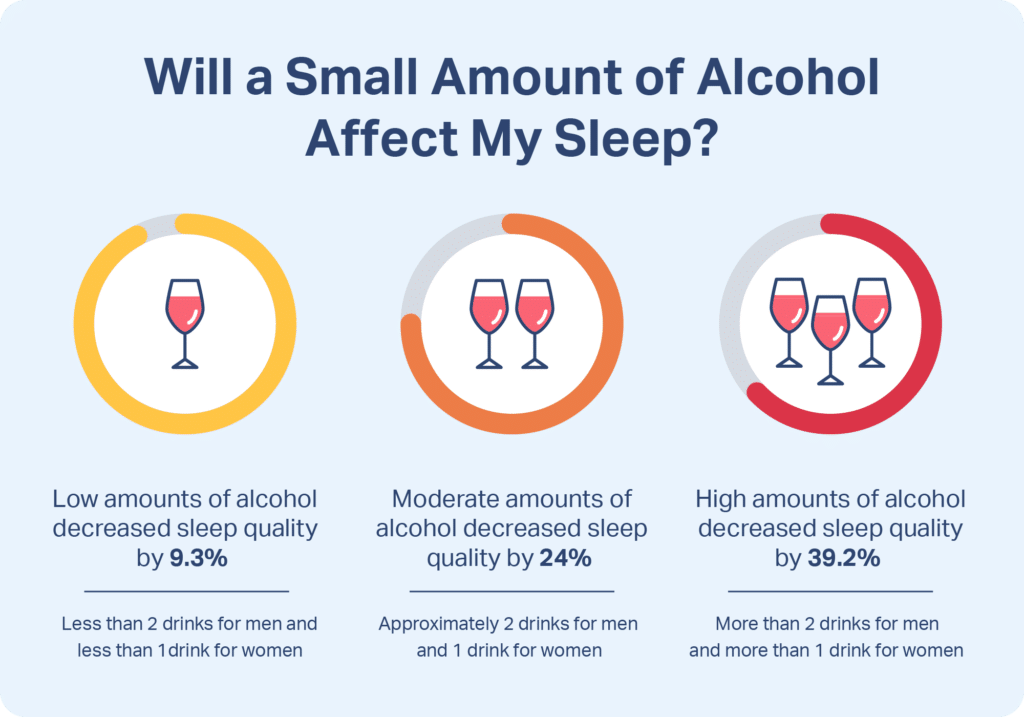
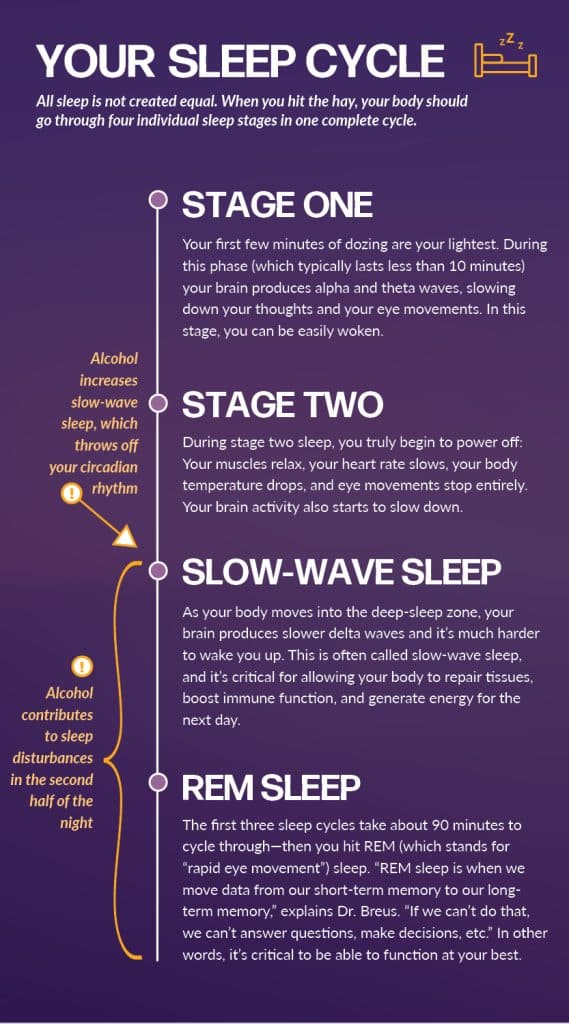
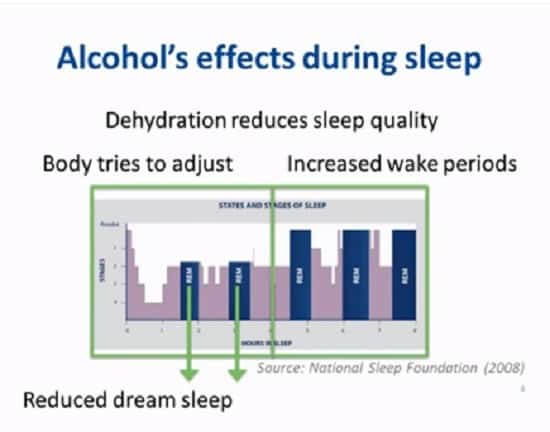
Alcohol and sleep are two seemingly unrelated elements that intertwine more than we may realize.
The effects of alcohol on sleep can be pretty surprising, and understanding how the two interact is essential for a good night’s rest.
From impairing sleep quality to disrupting the natural sleep cycle, alcohol’s impact reaches far beyond the initial nightcap.
This article explores the intriguing relationship between alcohol and sleep, shedding light on its effects and providing insights on achieving a truly restful night’s sleep.
This image is the property of www.sleepfoundation.org.
Review contents
Impact on Sleep Architecture
Alcohol’s impact on REM sleep
Alcohol significantly impacts the various stages of sleep, including REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep. REM sleep is a crucial part of the sleep cycle as it is associated with dreaming and plays a crucial role in memory consolidation and emotional processing. Unfortunately, alcohol consumption before bed can disrupt REM sleep. It reduces the amount of time spent in REM sleep and can cause a decrease in the overall quality of this stage of sleep. This disruption can lead to memory formation and emotional regulation difficulties, affecting our daily functioning.
Effect on slow-wave sleep
Another stage of sleep that is affected by alcohol is slow-wave sleep. Slow-wave sleep, also known as deep sleep or NREM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement) sleep Stage 3, is when the body rests and repairs itself. Slow brainwaves characterize it and are essential for the physical restoration and functioning of the immune system. However, alcohol consumption can suppress slow-wave sleep, reducing the amount and quality of this vital sleep stage. As a result, our bodies may not receive the necessary therapeutic benefits, which can leave us feeling fatigued and less energized the next day.
Influence on sleep cycles
Sleep is a cyclical process with distinct stages and cycles. Each sleep cycle typically includes a combination of light sleep, deep sleep, and REM sleep. Alcohol can disrupt the natural progression of these cycles. While alcohol initially acts as a sedative, promoting sleep onset, it can later disrupt the overall balance of sleep stages. As the sedative effects wear off, alcohol can lead to more fragmented and disrupted sleep cycles. This disruption can result in poorer sleep quality and leave us groggy and unrefreshed upon waking.
Sleep Onset and Sleep Latency
Alcohol’s sedative effect
Alcohol is commonly known for its soothing properties, which can help some individuals fall asleep more quickly. It reduces sleep onset latency, the time it takes to fall asleep once in bed. However, it is essential to note that even though alcohol may initially induce sleepiness, it does not promote the same level of restorative sleep that occurs during alcohol-free sleep. This soothing effect can create a false perception that alcohol is beneficial for sleep, leading to a potential reliance on alcohol as a sleep aid.
Decreased time we are taken to fall asleep.
One of the effects of alcohol is its impact on sleep latency or the time it takes to fall asleep. Alcohol can decrease sleep latency, causing individuals to fall asleep faster than without alcohol. This can appeal to those who struggle with insomnia or have difficulty winding down at the end of the day. However, while alcohol may help us fall asleep quickly, it ultimately disrupts the later stages of sleep, as discussed earlier. Therefore, relying on alcohol as a sleep aid can harm our sleep quality and health.
Fragmented Sleep and Nighttime Awakening
Disruptions to sleep continuity
Alcohol consumption can lead to fragmented sleep, characterized by multiple awakenings at night. While alcohol initially promotes drowsiness, it can later disrupt the normal progression of sleep stages, resulting in frequent awakenings during the night. These interruptions can lead to a disturbed sleep pattern, preventing us from achieving the deep, uninterrupted sleep necessary for rest and rejuvenation. Consequently, we may wake up groggy, unfocused, and less prepared to face the day ahead.
Increased frequency of waking up during the night
Alcohol consumption can significantly increase the frequency of nighttime awakenings. Even if we fall asleep quickly after drinking alcohol, we are more likely to wake up at night. These awakenings can be attributed to the disruption of sleep architecture, including the suppression of REM sleep and disturbances in slow-wave sleep. As a result, our sleep becomes fragmented, and we may experience difficulty getting back to sleep after each awakening, further impairing the overall sleep quality.
Sleep Disordered Breathing
Exacerbates sleep apnea symptoms
Alcohol poses a particular risk for individuals with sleep-disordered breathing, such as sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep, leading to interrupted sleep and oxygen deprivation. Alcohol can exacerbate sleep apnea symptoms by relaxing the muscles in the airway, further obstructing standard breathing patterns. This exacerbation can result in more severe and frequent incidents of interrupted breathing, leading to reduced sleep quality and potentially compromising overall health.
Breathing disturbances during sleep
Even for individuals without pre-existing sleep-disordered breathing conditions, alcohol can still disrupt standard respiratory patterns during sleep. Alcohol’s sedative effects can relax our throat and airway muscles, causing partial blockage or narrowing air passages.
This relaxation can result in snoring, wheezing, or other breathing disturbances during sleep. Such disruptions negatively impact our sleep quality, preventing us from experiencing the therapeutic effects of uninterrupted breathing and potentially causing daytime fatigue, irritability, and cognitive impairments.
This image is the property of www.paho.org.
Decreased Sleep Quality
Shallow and less restorative sleep
Alcohol consumption can lead to a decrease in the overall quality of our sleep. While alcohol’s sedative effects can help us fall asleep faster, they often lead to a shallow and less refreshing sleep experience. As discussed earlier, the disruption of REM and slow-wave sleep can prevent our bodies and brains from undergoing the necessary processes for physical and mental restoration during the night. Consequently, we wake up feeling less refreshed, struggle with daytime sleepiness, and may experience difficulty concentrating and focusing.
Impairments in sleep consolidation
Sleep consolidation refers to staying asleep throughout the night without frequent awakenings. Alcohol can impair this process by interrupting the standard sleep architecture and causing fragmented sleep. Instead of experiencing long stretches of uninterrupted sleep, alcohol can lead to multiple awakenings and difficulty maintaining continuous sleep. This impairment in sleep consolidation can leave us restless and unrefreshed in the morning, impacting our overall well-being and ability to function optimally during the day.
Effects on Sleep Duration
Alcohol’s impact on total sleep time
Alcohol consumption can directly impact the total duration of our sleep. While it may initially help us fall asleep faster, it can also reduce the overall length of our sleep. The disrupted sleep architecture and increased awakenings caused by alcohol can shorten the time we spend asleep, leading to a decrease in the total sleep duration. Inadequate sleep duration can contribute to feelings of fatigue, reduced cognitive function, and an increased risk of various health issues.
Altered sleep duration and sleep debt
Furthermore, alcohol can disrupt our sleep-wake schedule, leading to altered sleep duration patterns. It can cause us to go to bed later or wake up earlier than usual, resulting in less overall sleep time.
This alteration can accumulate over time, creating a sleep debt that needs to be repaid. When we consistently fail to obtain sufficient sleep and accumulate sleep debt, it can impact our energy levels, mood, cognitive performance, and overall health. Prioritizing adequate, uninterrupted sleep is crucial for maintaining optimal well-being.
This image is the property of www.priorygroup.com.
Delayed Circadian Rhythm
Disrupted internal body clock
Our body’s internal circadian rhythm regulates our sleep-wake cycle and various physiological processes. Alcohol can disrupt this delicate balance by altering the timing of our sleep-wake cycle. The sedative effects of alcohol may cause us to fall asleep earlier than usual, but as its effects wear off, it can result in a delayed circadian rhythm. This delay can make maintaining a consistent sleep schedule challenging and create difficulties in aligning our natural sleep-wake cycle with societal or work demands.
Shift in sleep-wake cycle timing.
Alcohol’s impact on the circadian rhythm can lead to a shift in our sleep-wake cycle timing. This shift can manifest as difficulty falling asleep at the desired bedtime or struggling to wake up at the intended wake-up time. As a result, our sleep patterns become erratic, leading to further sleep quality and duration disruptions. Consistency in sleep-wake times is crucial for maintaining a healthy circadian rhythm and promoting optimal sleep. Alcohol-induced disturbances to this rhythm can interfere with our overall sleep patterns and negatively impact our well-being.
Increased Risk of Sleep Disorders
Insomnia and alcohol-related sleep disorders
Alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing or exacerbating sleep disorders, particularly insomnia. Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and unable to return to sleep. While alcohol may initially act as a sedative and help us fall asleep faster, the disruptions in sleep architecture caused by alcohol consumption can lead to developing or worsening insomnia symptoms. Consequently, individuals may experience chronic sleep difficulties and require professional assistance to overcome these challenges.
Associations with sleep disturbances and disorders
In addition to insomnia, alcohol consumption has been associated with various other sleep disturbances and disorders. These include sleepwalking, sleep talking, night terrors, and restless legs syndrome.
Alcohol’s impact on the brain and the disruption it causes to standard sleep patterns can contribute to the occurrence or aggravation of these sleep-related issues. Understanding the connections between alcohol consumption and sleep disturbances can help individuals make informed choices about their sleep habits and prioritize healthier sleep practices.
This image is the property of d3srkhfokg8sj0.cloudfront.net.
Impact on Sleep-Related Health Issues
Effects on cardiovascular health
Alcohol’s effect on sleep can significantly impact our cardiovascular health. Disrupted sleep patterns caused by alcohol consumption can lead to increased blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, and cardiovascular disease risk. The suppression of deep sleep and REM sleep can impair critical restorative processes that promote cardiovascular health. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize the potential risks associated with alcohol consumption and take steps to promote healthy sleep habits and overall cardiovascular well-being.
Links to mental health conditions
Sleep and mental health are closely intertwined, and alcohol consumption can impact both aspects. Alcohol’s disruption of sleep architecture and circadian rhythm can contribute to developing or exacerbating mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression. Alcohol is often used as a coping mechanism for stress or emotional difficulties, further exacerbating the cycle of sleep disruption and mental health challenges. Prioritizing healthy sleep practices and seeking professional help can be critical in managing alcohol use and mental well-being.
Conclusion
Recap of alcohol’s effects on sleep
Alcohol consumption undoubtedly impacts various aspects of our sleep, including sleep architecture, onset and latency, continuity, sleep quality, duration, circadian rhythm, sleep disorders, and sleep-related health issues. It disrupts the balance of REM and slow-wave sleep, leads to fragmented sleep and increased awakenings, exacerbates sleep-disordered breathing, decreases sleep quality and consolidation, alters sleep duration patterns, delays the circadian rhythm, and increases the risk of sleep disorders and associated health issues.
Importance of prioritizing sleep quality and health
Recognizing the impact of alcohol on sleep is crucial for prioritizing our sleep quality and overall health. Ensuring we prioritize adequate, uninterrupted sleep is essential for physical and cognitive restoration, as well as emotional and psychological well-being.
Developing healthy sleep habits, such as maintaining consistent sleep-wake times, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and seeking professional help for sleep disorders or alcohol-related sleep challenges, can significantly improve our sleep quality and positively impact our overall quality of life.
Ultimately, the key lies in balancing our choices surrounding alcohol consumption and prioritizing healthy sleep habits to support optimal sleep and well-being.
This image is the property of cassioburycourt.com.