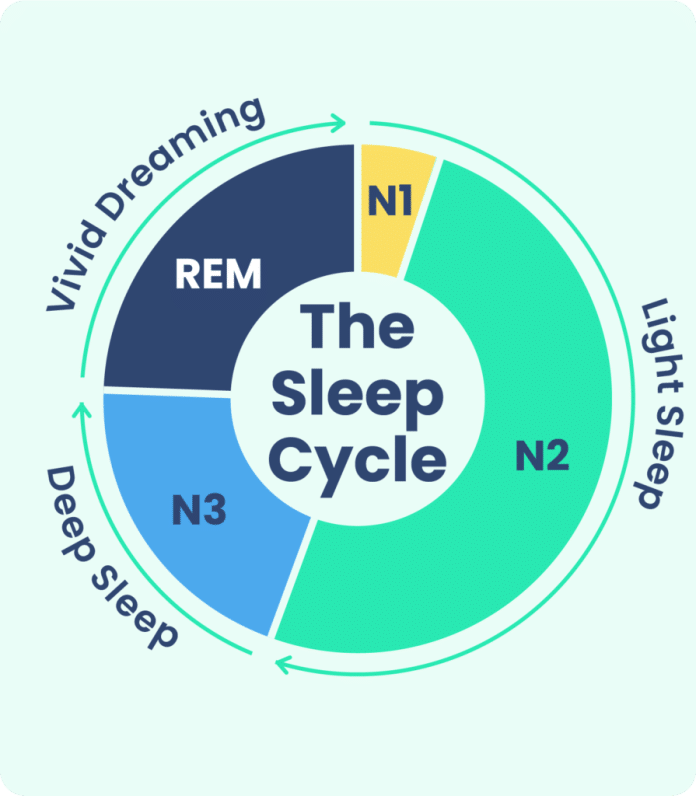
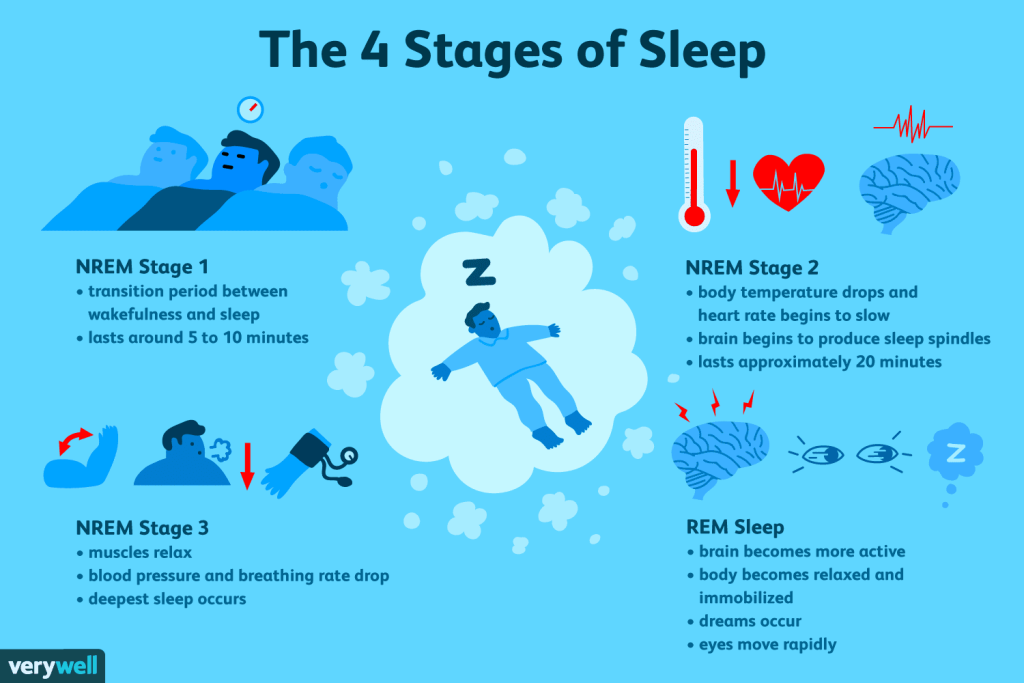
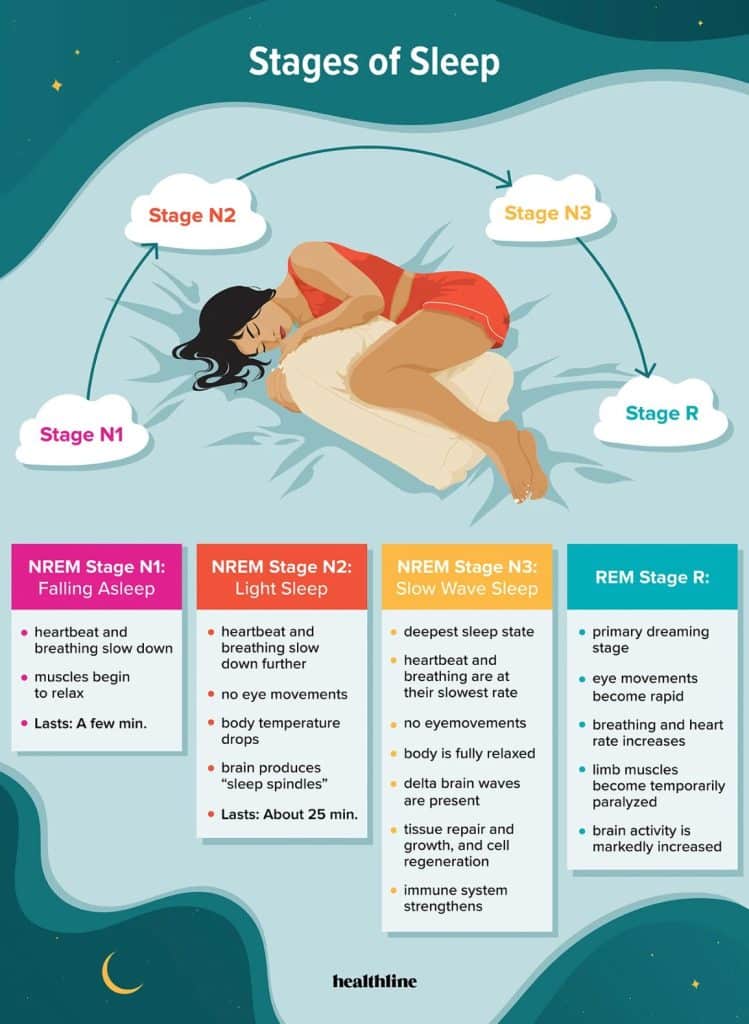
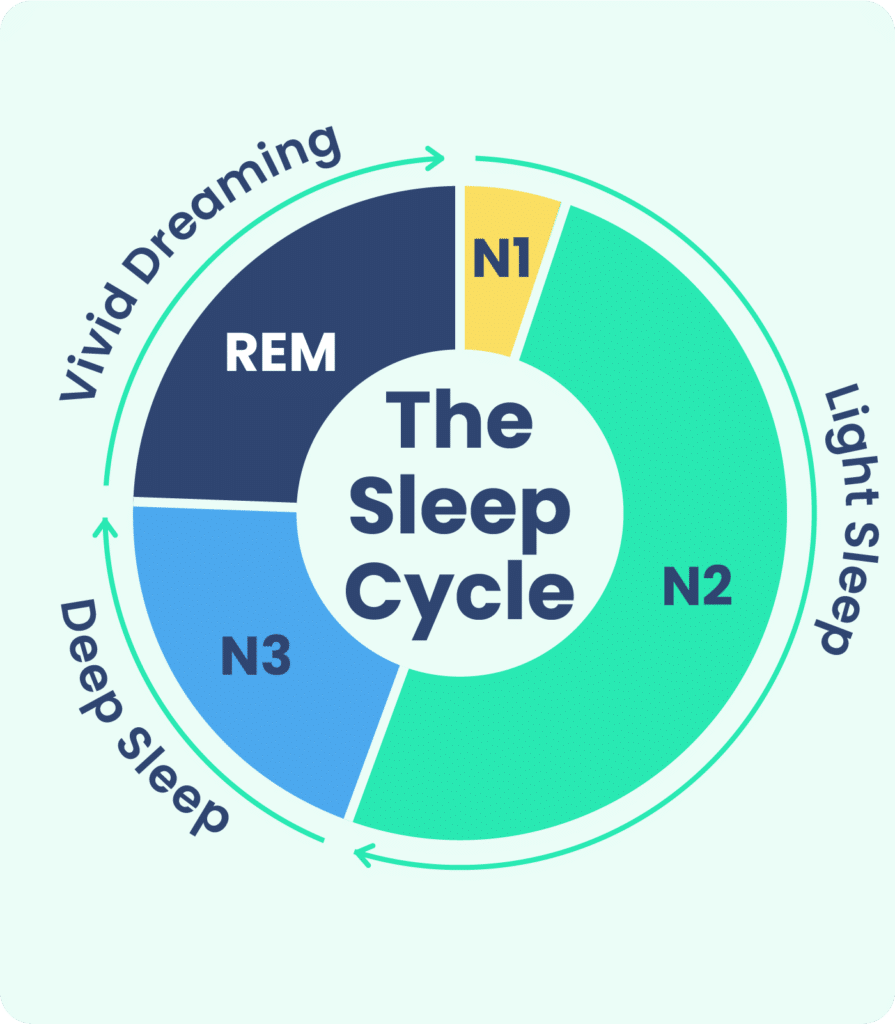
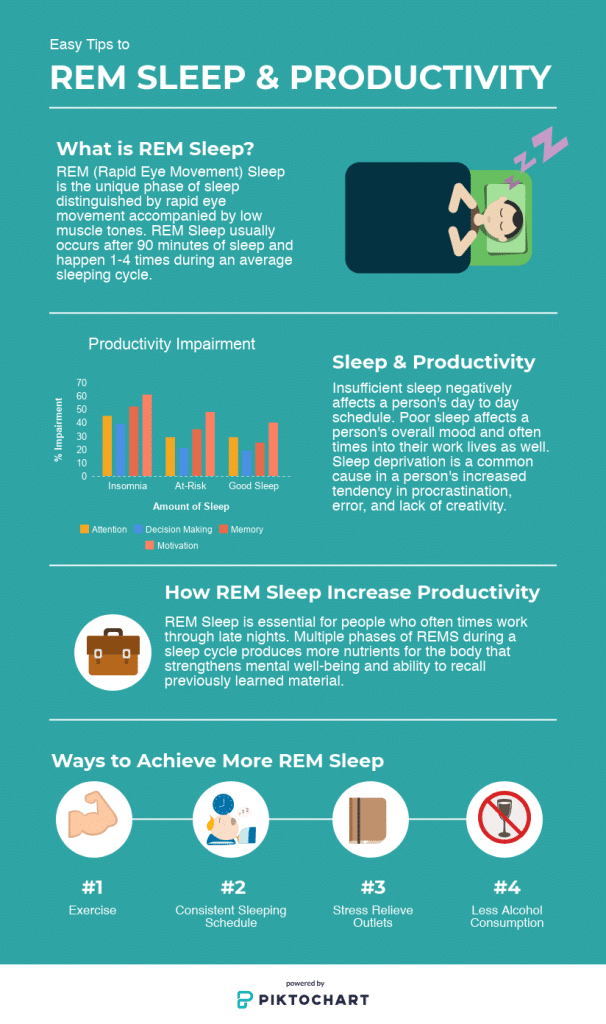
During REM sleep, your brain becomes highly active and resembles the same patterns as when you are awake. This stage of sleep is characterized by rapid eye movements (hence the name “REM”), vivid dreams, and temporary paralysis of your voluntary muscles. As your mind delves into the depths of your subconscious, your body remains immobile, ensuring that you don’t physically act out your dreams. Although the exact purpose and function of REM sleep are still being studied, it is widely believed to be crucial for memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and overall brain health.
Review contents
Brain Activity
During REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, there is a significant increase in brain activity. This is the stage of sleep where dreaming occurs, and it is marked by the brain being highly active, comparable to when you are awake. This increased brain activity is essential for the brain’s maintenance and development, as well as various cognitive processes.
Physical Characteristics
Muscle Paralysis
One distinctive physical characteristic of REM sleep is muscle paralysis. This temporary loss of muscle tone prevents you from acting out your dreams and ensures that you remain still while experiencing intense dream states. This paralysis is essential for your safety and the prevention of injury during sleep.
Rapid, Shallow Breathing
Another physical change during REM sleep is rapid and shallow breathing patterns. Your breathing becomes irregular and faster when compared to other stages of sleep, such as non-REM sleep. This heightened respiratory activity is attributed to the increased brain activity and the vivid dreaming experienced during REM sleep.
Irregular Heart Rate
In tandem with the rapid breathing, your heart rate also becomes irregular during REM sleep. The heart rate fluctuates, sometimes increasing and sometimes decreasing, as your body responds to the intense neural activity happening in your brain. This variation in heart rate is a normal occurrence during this stage of sleep.
Sleep Cycle
REM Sleep in the Sleep Cycle
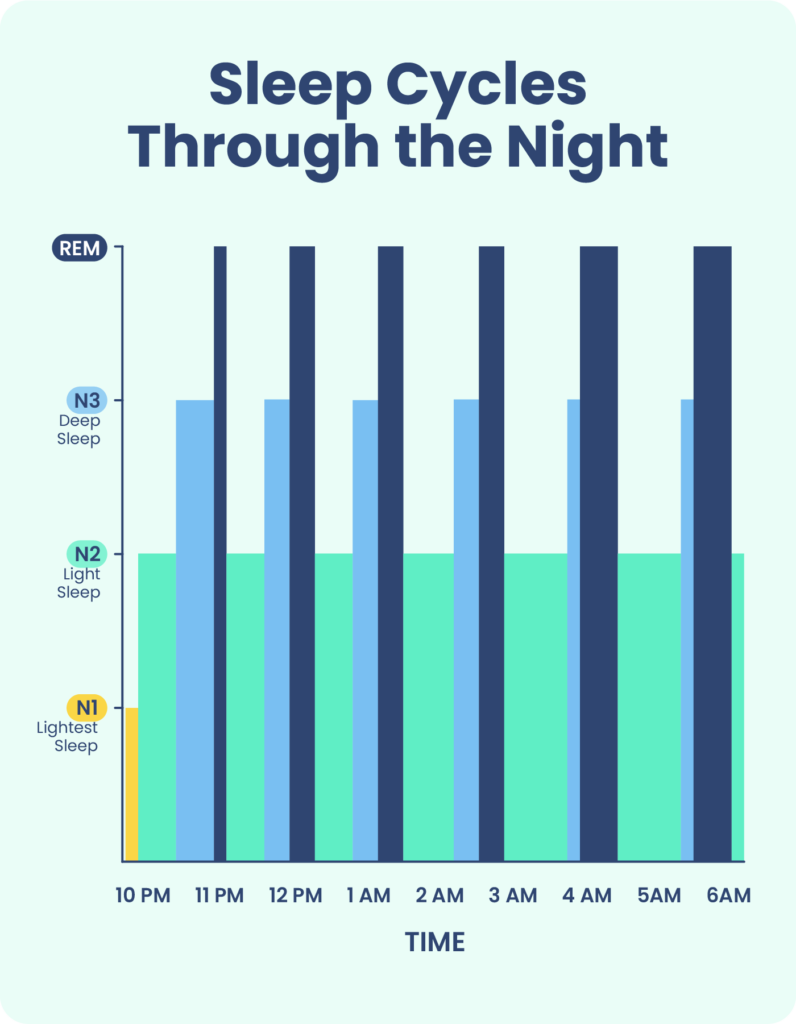
REM sleep is a crucial component of the sleep cycle, which consists of several distinct stages. It typically occurs after a period of non-REM sleep and is characterized by its high brain activity and rapid eye movement. The sleep cycle repeats throughout the night, with REM sleep becoming more prevalent as the night progresses.
Duration of REM Sleep
The duration of REM sleep varies throughout the sleep cycle. In the beginning, REM sleep episodes are shorter, usually lasting around 10 minutes. However, as the sleep cycle continues, the duration of REM sleep increases, with each episode potentially lasting up to an hour. This extended REM sleep later in the night is believed to be associated with more intense and vivid dreaming experiences.
Memory and Learning
Consolidation of Memories
REM sleep plays a vital role in the consolidation of memories. It is during this stage that the brain processes and stores information acquired during wakefulness. Research suggests that REM sleep specifically enhances the consolidation of emotionally charged memories, helping to solidify these experiences and their associated emotions.
Learning Enhancement
Not only does REM sleep aid in memory consolidation, but it also enhances learning. Studies have shown that individuals who experience high-quality REM sleep perform better in tasks involving creative problem-solving, critical thinking, and pattern recognition. This learning-enhancing aspect of REM sleep is crucial for cognitive development and overall mental well-being.
Emotional Processing
Emotional Regulation
REM sleep is closely associated with emotional regulation. It is during this stage that the brain processes and regulates emotions, helping to balance and stabilize your mood. Adequate REM sleep is believed to contribute to better emotional well-being and improved emotional resilience in daily life.
Processing Traumatic Experiences
REM sleep also plays a crucial role in processing traumatic experiences. During this sleep stage, the brain actively integrates and works through emotional events, assisting in the management of trauma-related memories. Insufficient REM sleep can hinder the brain’s ability to effectively process and cope with traumatic experiences, potentially leading to heightened emotional distress.
Hormonal Changes
Increased Release of Acetylcholine
REM sleep is characterized by an increased release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. This chemical messenger is essential for modulating brain activity and facilitating communication between neurons. The heightened release of acetylcholine during REM sleep contributes to the intense brain activation observed in this stage.
Decreased Release of Serotonin and Norepinephrine
Conversely, the release of serotonin and norepinephrine, two neurotransmitters associated with wakefulness and arousal, is significantly decreased during REM sleep. This reduction in these neurotransmitters helps to maintain the state of relaxation and muscle paralysis necessary for undisturbed sleep during this dream-rich period.
Benefits of REM Sleep
Restoration and Rejuvenation
REM sleep is crucial for the restoration and rejuvenation of the body and mind. It allows for the repair and growth of tissues, promotes immune system function, and replenishes energy levels. Adequate REM sleep is vital for maintaining overall health and ensuring optimal physical and mental functioning.
Brain Development in Infants
REM sleep plays a vital role in brain development, particularly in infants. During this stage, the brain undergoes significant growth and maturation, which contributes to vital cognitive and sensory processes. Healthy REM sleep patterns in infants are crucial for their neurological development and future cognitive abilities.
Creativity Enhancement
REM sleep has been associated with enhancing creativity and problem-solving abilities. The vivid and imaginative nature of dreaming during this stage can facilitate the generation of new ideas, artistic inspiration, and innovative thinking. Engaging in regular REM sleep can promote a more creative mindset and enhance overall cognitive flexibility.
Disorders and Disturbances
REM Behavior Disorder
REM behavior disorder (RBD) is a sleep disorder characterized by the absence of muscle paralysis during REM sleep, leading to acting out dreams physically. Individuals with RBD may exhibit various movements, including talking, punching, kicking, or jumping out of bed. This disorder can significantly disrupt sleep quality and pose a risk of injury to oneself or a bed partner.
Nightmares
Nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that can cause fear, anxiety, or distress, often waking you up abruptly. They typically occur during REM sleep and can be linked to past traumatic experiences, stress, or anxiety. Frequent or severe nightmares may disrupt sleep quality and contribute to ongoing sleep disturbances.
Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon that occurs when you temporarily experience an inability to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up. It usually happens during REM sleep, when muscle paralysis is present to prevent acting out dreams. Sleep paralysis can be accompanied by hallucinations, causing significant fear or confusion.
Insomnia
Insomnia is a sleep disorder that involves difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or both. Insomnia can affect both REM and non-REM sleep, leading to fragmented sleep patterns and inadequate rest. Sleep disturbances can disrupt the normal sleep architecture, including REM sleep, thereby affecting cognitive function, mood, and overall well-being.
REM Sleep Deprivation
Negative Impact on Cognitive Function
Deprivation of REM sleep can have detrimental effects on cognitive function. REM sleep is crucial for memory consolidation, learning enhancement, and cognitive processing. Without sufficient REM sleep, these cognitive functions may be compromised, leading to difficulties in memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities.
Mood Disturbances
Lack of REM sleep can significantly impact mood regulation. Emotional regulation and stability rely on the restorative properties of REM sleep. Emotional disturbances, irritability, and an increased susceptibility to stress are commonly experienced when REM sleep is consistently deprived.
Physical Health Effects
REM sleep deprivation can also have negative consequences on physical health. Since REM sleep promotes tissue repair, lack of it may impede the body’s natural healing processes and impair the immune system. Chronic REM sleep deprivation has been associated with an increased risk of developing various health conditions, including cardiovascular problems, obesity, and diabetes.
REM Sleep Disorders and Treatment
Diagnosis of REM Sleep Disorders
Diagnosing REM sleep disorders typically involves a comprehensive sleep evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and sleep studies. Polysomnography, a test that monitors various physiological parameters, can help identify abnormalities in REM sleep patterns and aid in the diagnosis of specific disorders.
Treatment Options for REM Sleep Disorders
Treatment options for REM sleep disorders depend on the specific condition and its underlying causes. For REM behavior disorder, medications such as clonazepam may be prescribed to help reduce physical movements during REM sleep. In cases of nightmares, therapy techniques like imagery rehearsal therapy or trauma-focused therapy can assist in reducing distressing dreams. Sleep hygiene practices, relaxation techniques, and lifestyle modifications are often recommended for managing sleep paralysis and insomnia related to REM sleep disturbances.
In conclusion, REM sleep is a critical stage of the sleep cycle that involves increased brain activity, dreaming, and unique physical characteristics. It plays a vital role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, hormonal changes, and overall well-being. Disturbances in REM sleep can lead to various disorders and have negative impacts on cognitive function, mood, and physical health. Seeking proper diagnosis and treatment for REM sleep disorders is essential in maintaining healthy sleep patterns and optimizing overall sleep quality and awareness of its importance is vital for a well-rounded understanding of a good night’s sleep.