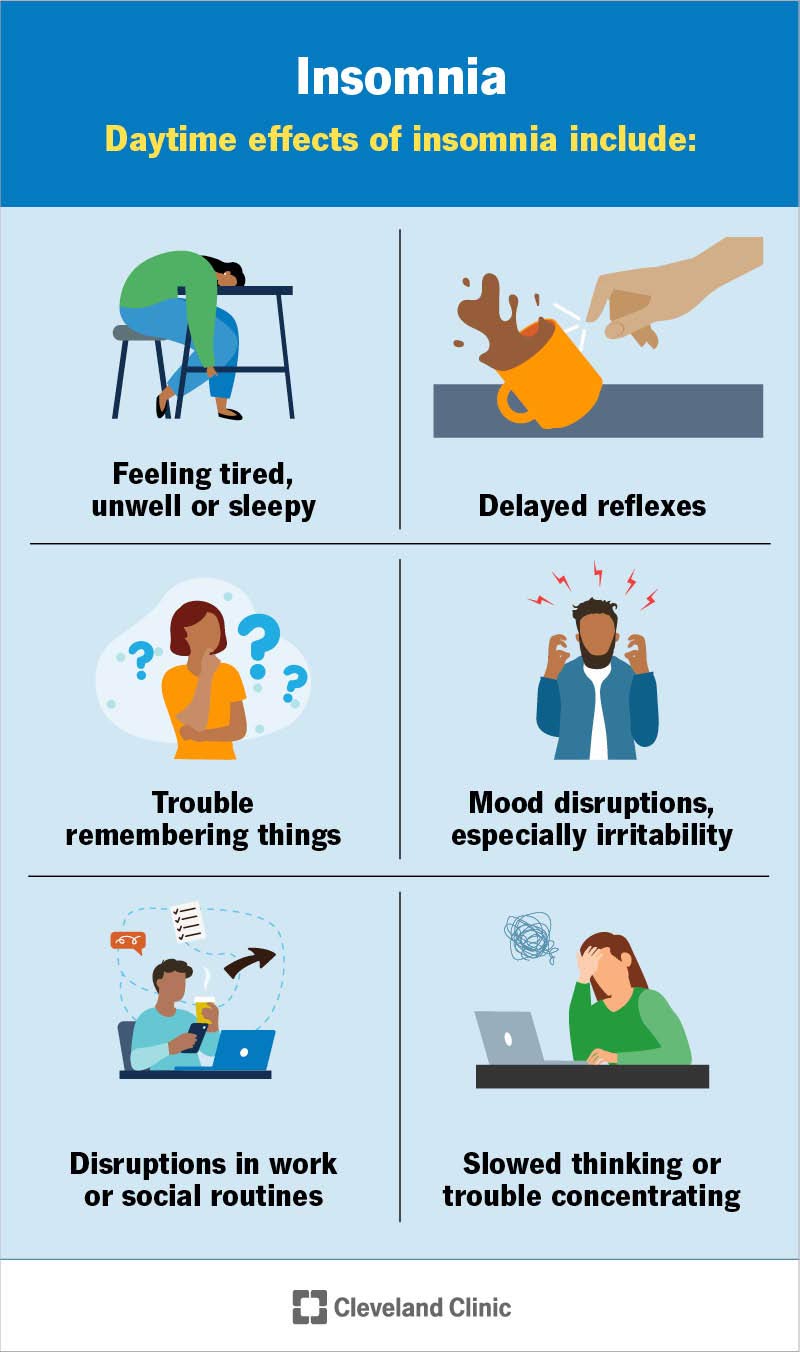
Are restless nights and sleepless hours starting to take a toll on your overall well-being? If so, you may be wondering what is behind this disruptive sleep pattern. In “What Causes Insomnia?”, we will explore the various factors contributing to this common sleep disorder. From stress and anxiety to lifestyle habits and underlying health conditions, understanding the causes of insomnia is the first step towards finding effective solutions and reclaiming a good night’s rest. So, let’s uncover the root causes and embrace a more peaceful slumber. Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that can have a significant impact on your overall well-being. It is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or both. If you’ve been struggling with insomnia, it’s important to understand the potential underlying causes. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the various factors that can contribute to insomnia and how they may be affecting your sleep.
Review contents
Psychological Factors
Stress and anxiety are among the leading psychological factors that can disrupt your sleep. When you’re under high levels of stress or experiencing excessive worry, it can be challenging to calm your mind and relax enough to fall asleep. Similarly, depression can also have a profound impact on your sleep patterns, often causing insomnia or excessive sleepiness.
Trauma, whether recent or in the past, can also be a significant contributor to insomnia. Those who have experienced a traumatic event may struggle with nightmares, flashbacks, or hyperarousal, making it difficult to achieve restful sleep. Psychiatric disorders, such as bipolar disorder or schizophrenia, can also disrupt sleep patterns and lead to insomnia.
Medical Conditions and Medications
Certain medical conditions and the medications used to treat them can interfere with sleep. Chronic pain conditions, like arthritis or fibromyalgia, can cause discomfort and make it challenging to find a comfortable sleep position. Respiratory disorders, such as asthma or sleep apnea, can also disrupt sleep by causing breathing difficulties or recurrent awakenings throughout the night.
Gastrointestinal problems, such as acid reflux or irritable bowel syndrome, can lead to discomfort or pain that affects sleep quality. Neurological conditions, like Parkinson’s disease or Alzheimer’s disease, can also disrupt sleep patterns. Additionally, hormonal imbalances, such as an underactive thyroid or hormonal fluctuations during menopause, can contribute to insomnia.
Certain medications have known side effects that can disrupt sleep. For example, medications used to treat conditions like asthma, high blood pressure, or allergies can contain stimulants that keep you awake. Antidepressants and steroids can also interfere with sleep patterns.
Lifestyle Factors
Your lifestyle choices and habits can greatly impact your sleep quality. Poor sleep habits, such as using electronic devices right before bed or engaging in stimulating activities, can make it difficult for your body to wind down and prepare for sleep. Similarly, an irregular sleep schedule, where you go to bed and wake up at different times each day, can disrupt your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
Caffeine and alcohol consumption can also have a significant impact on your sleep. Caffeine is a stimulant that can interfere with your ability to fall asleep and can stay in your system for several hours. While alcohol may initially make you feel drowsy, it can disrupt the later stages of sleep and lead to awakenings throughout the night.
Environmental factors, such as room temperature, noise levels, and light exposure, can also affect your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep. A room that is too hot or too cold, loud noises from outside or within your home, or excessive light exposure can all contribute to insomnia.
Sleep Disorders
In addition to the aforementioned factors, certain sleep disorders can directly cause insomnia. Sleep apnea, a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, can disrupt your sleep quality and lead to frequent awakenings. Restless leg syndrome, a neurological disorder characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move your legs, can cause discomfort and make it challenging to relax.
Narcolepsy, a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden bouts of sleep, can disrupt your ability to maintain a normal sleep schedule. Periodic limb movement disorder, which involves repetitive limb movements during sleep, can also lead to disturbances in sleep.
Age-Related Factors
As we age, our sleep patterns and needs naturally change. Older adults may experience a shift in their sleep-wake cycle, leading to an earlier bedtime and earlier wake-up time. This shift can make it difficult to obtain a sufficient amount of sleep and lead to insomnia.
Shift work sleep disorder is a condition that specifically affects individuals who work non-traditional hours, such as night shifts or rotating shifts. The irregular schedule and disruption to the body’s natural circadian rhythm can make it challenging to achieve restful sleep.
Menopause brings hormonal changes that can contribute to insomnia. Hot flashes and night sweats can disrupt sleep, and hormonal fluctuations during this stage of life can lead to increased difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
Genetic Predisposition
While it is difficult to determine the exact genetic factors that contribute to insomnia, research suggests that there may be a genetic predisposition to sleep disorders. Certain genetic variations may affect the regulation of sleep hormones or the functioning of the brain areas responsible for sleep. Understanding these genetic factors can help in the development of personalized treatment approaches for individuals struggling with insomnia.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes throughout life can have a significant impact on sleep. Pregnancy, for example, can bring about hormonal shifts that cause discomfort, frequent urination, and difficulty finding a comfortable sleep position. These factors can contribute to insomnia during pregnancy.
Menstruation can also affect sleep patterns. Hormonal fluctuations leading up to menstruation can cause mood swings, discomfort, and insomnia. Additionally, menopause brings about hormonal changes that can disrupt sleep, as mentioned earlier.
Jet Lag and Travel
Jet lag occurs when you travel across multiple time zones, disrupting your body’s internal clock. It can take several days for your body to adjust to the new time zone, leading to difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep. Factors such as disruption to your regular sleep schedule, exposure to different light and dark cycles, and the stress of travel can all contribute to insomnia during and after jet lag.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a crucial role in promoting healthy sleep. Noise levels, whether from traffic, construction, or other sources, can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. Likewise, excessive light exposure, such as bright streetlights or electronic devices emitting blue light, can interfere with your body’s production of melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate sleep.
Temperature can also affect your sleep quality. A room that is too hot or too cold can make it challenging to get comfortable and maintain an optimal sleeping environment.
Substance Abuse
Substance abuse, including nicotine, alcohol, and illegal drugs, can have a significant impact on sleep. Nicotine, a stimulant found in tobacco products, can interfere with your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep. Alcohol may initially make you feel drowsy, but it can disrupt the later stages of sleep and lead to frequent awakenings.
Illegal drugs can have various effects on sleep depending on the substance. Stimulant drugs can cause insomnia, while sedative drugs can lead to excessive sleepiness or disrupted sleep patterns.
In conclusion, insomnia can have numerous underlying causes, ranging from psychological factors to hormonal imbalances, medical conditions, lifestyle choices, and sleep disorders. Understanding these factors is crucial in identifying the root cause of your insomnia and developing an effective treatment plan. If you’re struggling with insomnia, consider consulting with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance in managing your sleep difficulties. Remember, a good night’s sleep is important for your overall health and well-being.