Nightmares can be pretty unsettling, leaving us feeling anxious and disturbed long after we wake up.
We all have experienced them at some point, but have you ever wondered what causes these terrifying dreams?
In this article, we will explore the various factors contributing to nightmares, shedding light on the mysterious realm of our sleeping minds. We will delve into stress, anxiety, trauma, medications, and certain foods, uncovering the reasons behind these haunting nocturnal visions. So, let’s find out what triggers our subconscious fears and unravels the enigma of nightmares.
Nightmares are distressing and vivid dreams that often leave us feeling scared, anxious, or unsettled upon waking up. While occasional nightmares are a normal part of sleep, experiencing them frequently can cause concern.
Various factors can contribute to nightmares, including stress, anxiety, sleep disorders, medications, substance use, food and beverages, sleep deprivation, psychological factors, environmental factors, sleep position, genetic predisposition, and even a specific disorder known as Nightmare Disorder.
This article will explore these factors in detail to better understand what causes nightmares and how they can be managed.
This image is the property of i0.wp.com.
Review contents
Impact of Stress on Sleep
Stress is a common trigger for nightmares and can significantly impact the quality of our sleep. When stressed, our brain remains active even during sleep, leading to greater dream intensity and frequent nightmares. ž
Additionally, stress can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters in our brain, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, which play a role in regulating sleep and dream patterns. Therefore, finding healthy ways to manage stress is essential, such as practicing relaxation techniques, exercising regularly, or seeking support from loved ones or healthcare professionals.
Effect of Anxiety on Dreams
Anxiety is closely related to stress and can similarly influence our dreams. Individuals with anxiety disorders often experience heightened levels of fear, worry, and unease, which can manifest in their dreams as nightmares.
Anxiety can also increase the likelihood of sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or restlessness, further contributing to nightmares. Managing anxiety through therapies, lifestyle changes, and medication can help alleviate its impact on our dreams.
PTSD and Nightmares
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a condition that arises after experiencing a traumatic event and is often characterized by intrusive thoughts, hyperarousal, and nightmares related to the traumatic experience.
Nightmares in individuals with PTSD can be vivid and recurring, causing significant distress and impeding their overall well-being. Treatment options for PTSD, including therapy, medications, and coping strategies, aim to reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares, providing relief to those affected.
Sleep Apnea and Nightmares
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, which can trigger micro-awakenings throughout the night and lead to fragmented sleep patterns. These disruptions can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares.
Sleep apnea patients often experience decreased oxygen levels, which can impact dream quality and increase the likelihood of nightmares. Proper management of sleep apnea, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, can improve sleep quality and reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
Insomnia and Its Connection to Bad Dreams
Insomnia, a condition characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, can also influence the prevalence of nightmares. Sleep fragmentation and poor sleep quality associated with insomnia can increase dream recall and a higher likelihood of experiencing distressing dreams. Treating underlying insomnia through cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) or other interventions can help minimize the occurrence of nightmares and promote restful sleep.
Restless Legs Syndrome and Nightmares
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disorder characterized by uncomfortable sensations in the legs, often accompanied by a relentless urge to move them. These symptoms typically worsen during rest or inactivity and can disrupt sleep.
Nightmares can occur in individuals with RLS due to the sleep disturbances caused by the constant need to move their legs. Managing RLS symptoms with lifestyle changes, medication, or other therapies can alleviate sleep disruptions and reduce the likelihood of nightmares.
This image is the property of sleepopolis.com.
Medications That May Cause Nightmares
Certain medications have been linked to an increased risk of nightmares. Antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can sometimes affect sleep and dream patterns, leading to more vivid or disturbing dreams.
Other medications, such as beta-blockers, anti-hypertensives, and over-the-counter drugs, may also have similar effects. Consulting with a healthcare professional about medication side effects and exploring alternative options if necessary can help minimize the occurrence of nightmares.
Nicotine, Alcohol, and Drug-Induced Nightmares
Substance use, including nicotine, alcohol, and drugs, can also influence our dream patterns and increase the likelihood of nightmares. Nicotine acts as a stimulant and can disrupt the natural sleep cycle, leading to more nightmares.
Excessive alcohol consumption can affect the duration and quality of REM sleep and the sleep stage associated with dreams and may trigger vivid or disturbing dreams. Additionally, certain drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system, can impact sleep patterns and contribute to nightmares. Reducing or eliminating substance use, especially before bedtime, can help alleviate nightmares related to these substances.
Spicy and Heavy Meals Before Bed
Eating spicy or heavy meals close to bedtime can cause indigestion, discomfort, and increased metabolism, disrupting sleep and leading to nightmares.
The body’s effort to digest a heavy meal can elevate body temperature and increase brain activity, which may result in more intense dreams. Consuming lighter meals and avoiding spicy foods before sleep can promote better digestion and reduce the likelihood of nightmares.
This image is the property of sleepopolis.com.
Caffeine and Nightmares
Caffeine is a stimulant that can interfere with our ability to fall asleep and maintain restful sleep. Consuming caffeinated beverages or foods close to bedtime can lead to sleep disturbances, including increased dream recall and potential nightmares. Limiting caffeine intake, especially in the evening, is advisable to promote better sleep quality and minimize the occurrence of nightmares.
Alcohol and Dream Disturbances
While alcohol may initially have a soothing effect, it can disrupt sleep patterns later at night. As blood alcohol levels decrease, the body may experience withdrawal symptoms, leading to sleep disturbances and heightened dream activity. Alcohol’s impact on REM sleep can result in more vivid, intense, or disturbing dreams. Moderating alcohol consumption and maintaining healthy drinking habits can help reduce alcohol-related dream disturbances.
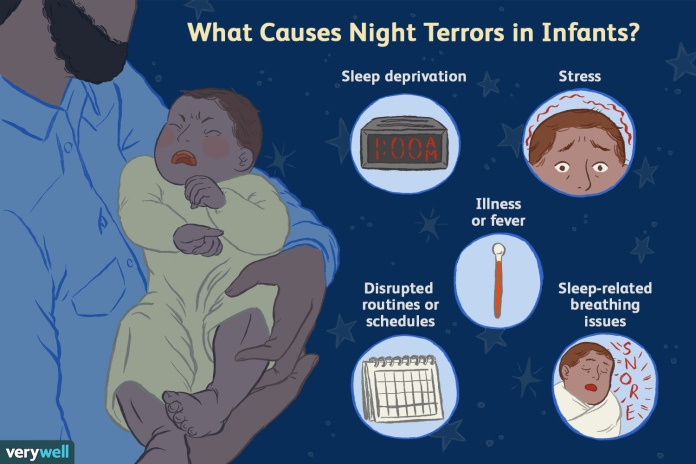
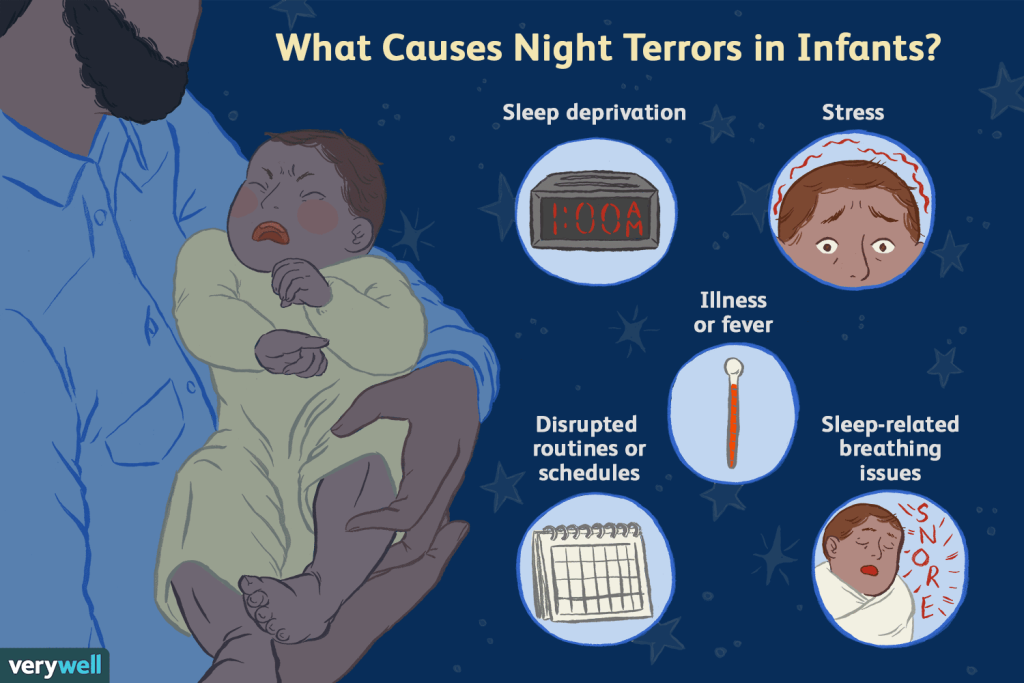
Impact of Lack of Sleep on Dream Patterns
Sleep deprivation, whether due to a busy lifestyle, shift work, or other factors, can alter dream patterns and make nightmares more prevalent. When we do not get enough sleep, our brain compensates by increasing the amount of REM sleep we experience, which is associated with dreaming.
This increased REM sleep can result in more vivid dreams, including nightmares. Prioritizing sleep and establishing consistent sleep routines can ensure adequate sleep and reduce nightmares caused by sleep deprivation.
This image is the property of www.verywellfamily.com.
REM Rebound and Intense Dreaming
REM rebound occurs when we are deprived of REM sleep and subsequently experience longer and more intense periods of REM sleep during subsequent nights. This phenomenon can lead to an increase in vivid dreams, including nightmares. Restoring regular sleep patterns and addressing any underlying causes of REM sleep disruption can reverse the REM rebound effect and alleviate nightmares.
Sleep Disorders Leading to Inadequate Sleep
Various sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy, periodic limb movement disorder, and circadian rhythm disorders, can cause inadequate sleep and contribute to nightmares. These disorders disrupt standard sleep architecture, leading to fragmented or disrupted sleep, which can increase dream intensity and frequency. Identifying and treating the underlying sleep disorder can help restore healthy sleep patterns and alleviate nightmares.
Repressed Emotions and Nightmares
Repressed emotions can find an outlet in dreams, particularly in nightmares. Unresolved or unexpressed feelings, such as fear, anger, guilt, or trauma, can manifest as frightening or distressing scenarios in our dreams. Engaging in therapy, journaling, or other emotional release practices can help process repressed emotions, reducing their influence on our dreams.
This image is the property of www.sleephealthfoundation.org.au.
Traumatic Experiences and Recurrent Nightmares
Experiencing a traumatic event can have a lasting impact on our dream life. Trauma-related nightmares often depict distressing or traumatic events and can frequently recur, causing significant distress. Therapies specifically designed to address trauma, such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) or trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy (TF-CBT), can help individuals process and cope with traumatic experiences, reducing the frequency and intensity of related nightmares.
Mental Health Disorders and Dream Disturbances
Certain mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia, can disrupt sleep patterns and influence dream content. Depression, for example, is associated with increased dream recall and more negative dreams, which may include nightmares. Managing underlying mental health conditions through therapy, medication, and self-care can help regulate sleep and improve dream quality.
Temperature and Nightmares
Extreme temperatures, whether too hot or cold, can disrupt sleep and impact dream patterns, potentially leading to nightmares. Uncomfortably warm or cold sleeping environments can trigger physiological and mental discomfort, which may manifest in our dreams. Maintaining a moderate and comfortable sleeping temperature can contribute to more restful sleep and reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
Noise and Dream Disruptions
Loud or repetitive noises in our environment while sleeping can interrupt the sleep cycle and disturb dream patterns. Sudden or alarming sounds can make their way into our dreams and lead to nightmares. Creating a quiet and peaceful sleep environment, using earplugs or sound machines if necessary, can help minimize noise-related dream disruptions.
Uncomfortable Sleeping Conditions
Physical discomfort resulting from uncomfortable bedding, unsupportive pillows, or an unfavorable sleeping position can contribute to sleep disturbances and nightmares. Creating a comfortable sleep environment is essential by ensuring a proper mattress and pillow, using bedding materials that suit our preferences, and adopting a sleeping position that promotes restful sleep. Investing in quality sleep accessories and optimizing sleeping conditions can enhance sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of nightmares.
Impact of Sleeping on the Back or Stomach
Sleeping positions can also affect dream intensity. Sleeping on the back or stomach has been associated with a higher incidence of nightmares than sleeping on the side. These positions can cause increased pressure on internal organs or lead to sleep apnea, thus influencing dream patterns. Experimenting with different sleeping positions and finding the one that provides the most comfortable and restful sleep can help reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
Sleeping in Uncomfortable Positions and Dream Intensity
Apart from specific sleeping positions, uncomfortable or awkward ones can impact dream intensity. Disrupted or restricted blood flow, muscle tension, or joint discomfort caused by sleeping in an unnatural position can lead to more vivid or unsettling dreams. Ensuring proper body alignment and support during sleep can improve sleep experience and reduce the likelihood of nightmares.
Family History and Nightmares
Genetic predisposition can play a role in the occurrence of nightmares. If we have family members who frequently experience nightmares, we may be more susceptible to having nightmares ourselves. While the exact mechanisms behind this genetic link are not fully understood, familial patterns in dream recall and nightmare frequency have been observed. Knowing our family history can help us better understand our susceptibility to nightmares and inform effective prevention and management strategies.
Inherited Sleep Disorders and Dream Disturbances
In addition to a potential genetic predisposition to nightmares, certain inherited sleep disorders may contribute to dream disturbances. Sleep disorders such as REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) or genetic conditions like narcolepsy with cataplexy can involve abnormal dream activity and increase the likelihood of nightmares. Identifying and treating these underlying sleep disorders can alleviate the impact of dream disturbances.
Nightmare Disorder: Definition and Symptoms
Nightmare Disorder is a specific sleep disorder characterized by recurrent nightmares that significantly disturb one’s sleep and cause distress or impairment in daily functioning. To be diagnosed with Nightmare Disorder, the nightmares must occur frequently (typically more than once a week), cause significant distress, and cannot be better explained by another sleep disorder, medical condition, medication, substance use, or mental health disorder. Other associated symptoms may include fear of falling asleep, difficulty falling back asleep after a nightmare, or daytime fatigue.
Causes and Risk Factors of Nightmare Disorder
Nightmare Disorder can be influenced by various factors, including those previously discussed, such as stress, anxiety, trauma, medications, and sleep disorders. Certain risk factors may also increase the likelihood of developing Nightmare Disorder, including a history of trauma or abuse, a family history of nightmares or sleep disorders, and certain mental health conditions such as depression or anxiety disorders. Understanding these causes and risk factors can help guide appropriate treatment and management strategies.
Treatment Options for Nightmare Disorder
Several treatment options for Nightmare Disorder are available to reduce nightmare frequency, intensity, and associated distress. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for nightmares (CBT-N) is often recommended as the first-line treatment, which involves techniques such as exposure therapy, image rehearsal therapy, and cognitive restructuring. Medication, targeted explicitly for nightmare reduction, may also be considered in some instances. Working closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment approach based on individual circumstances is essential.
In conclusion, nightmares can significantly impact our overall well-being and quality of sleep. Understanding the various factors that can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares, including stress, anxiety, sleep disorders, medications, substance use, food and beverages, sleep deprivation, psychological factors, environmental factors, sleep position, genetic predisposition, and Nightmare Disorder, can help us identify potential triggers and implement appropriate strategies to manage and reduce nightmares.
By prioritizing our sleep health and addressing any underlying causes or related conditions, we can work towards achieving restful and dream-filled nights that leave us feeling refreshed and rejuvenated.