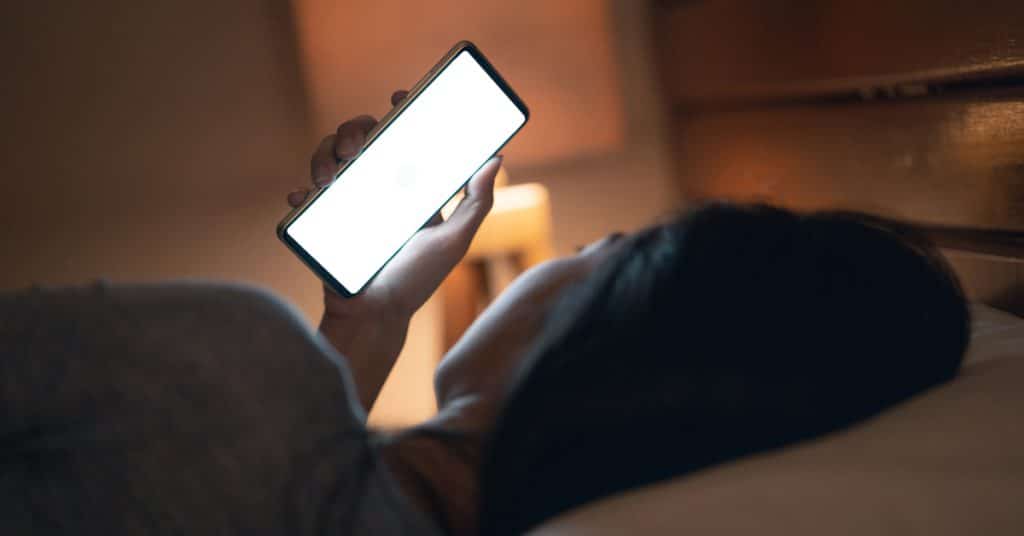
In today’s digital age, our world is constantly buzzing with screens and devices that entice us to stay connected 24/7.
However, there is a lingering concern that the excessive use of electronics before bedtime may harm our sleep quality and overall well-being.
We all love scrolling through our social media feeds or binge-watching the latest series on our tablets, but have we ever paused to consider the potential consequences of this electronic addiction?
This article explores the impact of using electronics before sleep and whether it disrupts our slumber.
This image is the property of www.sleephealthfoundation.org.au.
Review contents
Adverse Effects on Sleep Quality
Disruption of Circadian Rhythm
Using electronics before sleep can significantly disrupt our body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, known as the circadian rhythm. Our circadian rhythm is regulated by exposure to light, and the blue light emitted by electronic devices, such as smartphones and laptops, can interfere with this delicate balance. Exposure to blue light before bed can confuse our internal clock, leading to difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep throughout the night.
Suppression of Melatonin Production
Melatonin is a hormone that helps regulate our sleep-wake cycle and promotes sleep onset. However, using electronic devices before bedtime can suppress melatonin production, making it harder for us to fall asleep. The blue light emitted by these devices inhibits the release of melatonin, further disrupting our natural sleep patterns and compromising the quality of our sleep.
Increase in Blue Light Exposure
Electronic devices emit high levels of blue light, which is most effective at suppressing melatonin production and disrupting our circadian rhythm. Excessive exposure to blue light can affect the quality and duration of our sleep, leaving us feeling dizzy, tired, and less refreshed in the morning. Increased exposure to blue light can lead to insomnia and other sleep disorders if not appropriately managed.
Promotion of Sleep Disorders
The use of electronics before sleep has been linked to developing and exacerbating various sleep disorders. Conditions such as insomnia, restless leg syndrome, and sleep apnea can be worsened by using electronic devices in the evening. The overstimulation caused by engaging with screens before bed can make it harder for our bodies to relax and wind down, preventing us from entering a restorative state of sleep.
Impact on Brain Function
Impaired Cognitive Performance
Using electronics before sleep can impair our cognitive performance the following day. The blue light exposure and disrupted sleep caused by screen time can result in decreased alertness, attention span, and overall cognitive abilities. Our ability to focus, concentrate, and think clearly may suffer, affecting our productivity and performance in daily tasks.
Reduced Attention Span
Excessive screen time before bed can reduce attention, making it harder to stay engaged and focused on tasks. This can impact our ability to learn, retain information, and perform academically or professionally. The constant stimulation from electronic devices can contribute to a scattered and easily distracted mind, hindering our ability to concentrate on essential tasks.
Adverse Effect on Memory Formation
Proper sleep is crucial for memory consolidation and the formation of new memories. However, using electronics before sleep can disrupt this process, leading to memory formation and retention difficulties. The overstimulation from screens can interfere with the brain’s ability to process and store information, diminishing our ability to recall facts or events accurately.
Relationship with Mental Health
Increased Risk of Depression
Research has shown a correlation between excessive use of electronics before sleep and an increased risk of depression. The disrupted sleep patterns and negative impact on brain function caused by electronic devices can contribute to feelings of fatigue, lethargy, and emotional instability, which are common symptoms of depression. The constant exposure to screens can also exacerbate feelings of loneliness and isolation, further impacting our mental well-being.
Worsening of Anxiety Symptoms
Using electronics before bed can worsen anxiety symptoms, making relaxing and falling asleep harder. Constantly engaging with screens can keep our minds active and stimulated, increasing feelings of restlessness and worry. The blue light from electronic devices can also disrupt the body’s natural stress response, preventing us from adequately winding down and preparing for a good night’s sleep.
Higher Chances of ADHD Development
Excessive screen time before bed has been associated with an increased risk of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents. The overstimulation and disrupted sleep patterns caused by electronic devices can affect the development and functioning of the prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain responsible for attention, impulse control, and executive functions. This can contribute to the symptoms of ADHD, such as difficulty paying attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
Physical Health Consequences
Eye Strain and Visual Problems
Using electronics before sleep can strain our eyes and contribute to visual problems. Staring at screens for prolonged periods can cause eye fatigue, dryness, and irritation. The blue light emitted by electronic devices can also lead to digital eye strain, which includes symptoms such as blurred vision, headaches, and difficulty focusing. Prolonged exposure to digital screens before bed can worsen these symptoms and affect our overall eye health.
Musculoskeletal Issues
Propping ourselves in bed with electronic devices or using them in uncomfortable positions can lead to musculoskeletal issues. Hunching over screens or holding them in awkward positions can strain our neck, back, and shoulders, causing discomfort and potential long-term posture problems. It is essential to maintain proper posture and take regular breaks when using electronic devices to minimize the risk of developing musculoskeletal issues.
Obesity and Unhealthy Eating Patterns
Electronic devices before sleep have been linked to an increased risk of obesity and unhealthy eating patterns. The blue light emitted by screens can disrupt our body’s natural hunger and satiety cues, leading to an increased appetite and cravings, particularly for high-calorie and sugary foods.
Additionally, the passive nature of screen time can contribute to a lack of physical activity, further increasing the risk of weight gain and related health issues.
This image is the property of www.sclhealth.org.
Social and Interpersonal Consequences
Disrupted Sleep Patterns in Relationships
Using electronics before bed can disrupt sleep patterns for individuals and those sharing the same sleeping environment. The use of screens can lead to differences in sleep-wake schedules, causing conflicts and difficulties in synchronizing sleep routines. This can strain relationships, hinder quality time spent together, and affect overall communication and emotional connection within the relationship.
Negative Impact on Communication and Social Skills
Excessive use of electronics before sleep can hurt communication and social skills. Engaging with screens right before bed can limit opportunities for meaningful interactions and conversations with family members or partners. It can also contribute to disconnection from the real world, leading to social isolation and deteriorating interpersonal relationships.
Reduced Productivity at Work or School
Using electronics before bed can negatively affect productivity and performance at work or school the next day. Disrupted sleep, impaired cognitive function, and reduced attention span can make it harder to focus, concentrate, and complete tasks efficiently. This can lead to decreased productivity, increased errors, and difficulty meeting deadlines or academic requirements.
Ways to Minimize the Negative Effects
Establish a Digital Curfew
Setting a specific time to turn off all electronic devices before bed can help establish a digital curfew. By creating a cut-off point for screen time, we give our brains time to wind down and prepare for sleep. Avoiding screens for at least one hour before bed is recommended to allow our bodies to adjust naturally to the dark and promote melatonin production.
Use Night Mode and Blue Light Filters
Most electronic devices now offer night mode or blue light filters that can reduce the harmful effects of blue light on sleep. These settings can adjust the color temperature of screens, making them warmer and less stimulating to the brain. Enabling night mode or using blue light filters can help minimize the disruption to our circadian rhythm and enhance our ability to fall asleep more easily.
Practice Relaxation Techniques Before Bed
Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or gentle stretching, before bed can help calm our minds and prepare our bodies for sleep. Taking a few minutes to unwind and mentally transition from the stimulation of electronic devices to a more relaxed state can promote better sleep quality and alleviate any tension or stress that may hinder our ability to fall asleep.
Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule is essential for maintaining a healthy sleep routine and minimizing the adverse effects of electronic device usage before bed. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends, can help regulate our circadian rhythm and promote better sleep quality. Creating a sleep-friendly environment, such as keeping the bedroom calm, dark, and quiet, can support a consistent sleep schedule.
This image is the property of i.ytimg.com.
Alternatives to Electronics Before Sleep
Reading Books or Magazines
Reading a book or magazine before bed can be a great alternative to electronic devices. Reading can help relax our minds, divert our attention away from screens, and promote a sense of calm. Choosing printed materials instead of electronic versions allows us to avoid blue light exposure and can enhance our overall sleep experience.
Listening to Soothing Music
Listening to soothing music or guided relaxation audio can help us unwind and create a peaceful atmosphere before sleep. Music has been shown to impact our emotions directly and can induce relaxation, making it easier to fall asleep. Using headphones or a speaker can provide a more immersive experience and block out any external noise that may disrupt our sleep.
Engaging in Light Stretching or Yoga
Engaging in light stretching or yoga before bed can help release muscle tension and promote physical and mental relaxation. Gentle stretching exercises and yoga poses can help prepare our bodies for sleep by relieving any physical discomfort or stiffness accumulated throughout the day. This mindful movement can also help shift our focus away from electronic devices and create a peaceful pre-sleep routine.
Keeping a Journal or Doing Puzzles
Keeping a journal or engaging in puzzles and brain teasers before bed can be a mentally stimulating yet screen-free alternative. Writing down our thoughts, feelings, or tasks for the next day in a journal can help declutter our minds and promote a sense of calm.
Similarly, engaging in puzzles, crosswords, or sudoku can divert our attention away from screens and provide a mental workout that can tire our minds and prepare us for sleep.
In conclusion, using electronics before going to sleep can adversely affect our sleep quality, brain function, mental health, physical health, and social well-being. The disruption of our circadian rhythm, suppression of melatonin production, increase in blue light exposure, and promotion of sleep disorders are just a few of the consequences of excessive screen time before bed.
Establishing a digital curfew, using night mode and blue light filters, practicing relaxation techniques, and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule are recommended to minimize these adverse effects.
Additionally, exploring alternatives to electronics such as reading books, listening to soothing music, engaging in light stretching or yoga, and keeping a journal or doing puzzles can provide healthier and more sleep-friendly activities before bedtime. We can enhance our overall well-being and promote healthier sleep habits by prioritizing our sleep hygiene and reducing our reliance on electronic devices before sleep.