Sleep deprivation is a common issue many of us experience at some point in our lives, yet it often goes unnoticed or dismissed as a regular part of our busy schedules.
In this article, we explore the signs of sleep deprivation that we should all be aware of, as it can significantly impact our physical and mental well-being.
From feeling constantly tired to experiencing difficulty concentrating and even mood swings, recognizing the signs is the first step towards ensuring a good night’s sleep and a healthier and more balanced life.
Review contents
Physical Signs of Sleep Deprivation
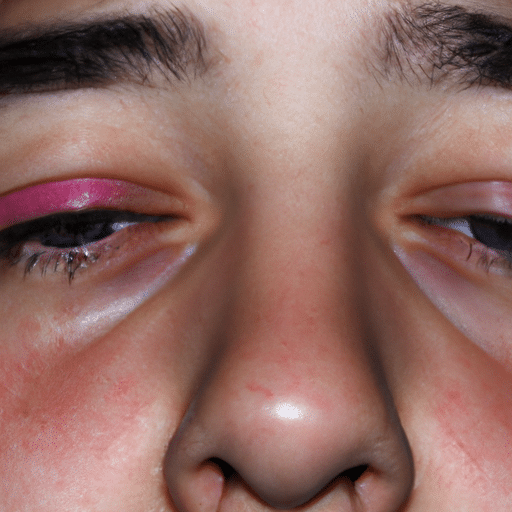
Eyes
When we are sleep-deprived, our eyes can give us some telltale signs. One common physical sign is redness and bloodshot eyes. Lack of sleep can cause the blood vessels in the eyes to enlarge, leading to a red appearance. Additionally, our eyes may become puffy and swollen, with dark circles forming under them. These visible signs are often a result of fluid retention and increased inflammation due to sleep deprivation.
Skin
Our skin can also show signs of sleep deprivation. Our skin may appear dull and lackluster when we don’t sleep enough. This is because sleep is crucial for skin cell regeneration and repair. Without adequate rest, our skin’s rejuvenation is compromised, leading to a tired and aged appearance. Sleep deprivation can also contribute to increased wrinkles, fine lines, and dark under-eye circles, further affecting our overall complexion.
Appetite and Weight
Sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on our appetite and weight. When sleep-deprived, our hormone levels can become imbalanced, particularly the hormones that regulate hunger – ghrelin and leptin. This imbalance can increase feelings of hunger and cravings for high-calorie and sugary foods. Moreover, sleep deprivation can disrupt our body’s ability to metabolize carbohydrates, leading to weight gain over time.
Muscle Pain and Weakness
One of the physical signs of sleep deprivation is muscle pain and weakness. Sleep is essential for the repair and rejuvenation of our muscles. When we don’t get enough sleep, our muscles may not fully recover, resulting in muscle fatigue and soreness. This can make even simple tasks feel strenuous and exhausting. Sleep deprivation can also affect our muscle coordination and balance, making us more prone to accidents and injuries.
Headaches
Frequent headaches are another physical sign of sleep deprivation. When we are sleep-deprived, the blood vessels in our brain can dilate, causing increased pressure and tension, leading to headaches. Lack of sleep can also trigger migraines or make existing migraines more severe. These headaches can be debilitating, making concentrating, working, or engaging in daily activities challenging.
Behavioral Signs of Sleep Deprivation
Inattentiveness and Poor Concentration
One of the behavioral signs of sleep deprivation is a noticeable decline in attentiveness and poor concentration. When we are sleep-deprived, it becomes difficult to focus on tasks, retain information, and stay engaged. Our ability to concentrate is impaired, affecting our productivity and performance at work, school, or other activities that require mental focus.
Moodiness and Irritability
Sleep deprivation can significantly impact our mood, leading to increased moodiness and irritability. When we don’t get enough rest, our emotions may become more volatile, and we may find ourselves easily annoyed or angered by minor things. This emotional instability can strain relationships and make interacting with others positively and harmoniously challenging.
Lack of Motivation and Productivity
A lack of sleep can drain our motivation and hinder our productivity. When we are sleep-deprived, finding the drive and energy to complete tasks becomes harder. We may feel sluggish, unmotivated, and unable to perform at our best. Additionally, sleep deprivation can impair our cognitive functions, making it even more challenging to engage in complex or demanding activities.
Impaired Memory and Cognitive Functions
Sleep deprivation can have a detrimental effect on our memory and cognitive functions. Our ability to retain information, recall details, and process new knowledge can be compromised when we don’t sleep enough. Sleep plays a vital role in consolidating memories and strengthening neural connections in the brain. Without adequate rest, our memory formation and overall cognitive performance suffer.
Increased Risk-Taking Behavior
When we are sleep-deprived, our decision-making abilities can be impaired, leading to increased risk-taking behaviors. Sleep deprivation can alter our judgment and make us more prone to impulsive actions. We may engage in activities that we would typically consider risky without thoroughly considering the potential consequences. This behavioral change can negatively affect our safety and overall well-being.
Emotional Signs of Sleep Deprivation
Depression and Anxiety
Sleep deprivation is closely linked to developing or exacerbating mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. When sleep-deprived, our brain chemistry becomes imbalanced, affecting our mood and emotional well-being. Prolonged sleep deprivation can increase the risk of experiencing depressive episodes or heightened anxiety symptoms. It is essential to prioritize adequate sleep to support our mental health and emotional stability.
Emotional Instability
Sleep deprivation can make us more emotionally reactive and prone to emotional instability. When we are sleep-deprived, our emotional regulation becomes compromised, causing us to experience heightened emotions. We may get easily overwhelmed, excessively anxious, or excessively sad. These emotional fluctuations can impact our relationships and make it difficult to navigate daily challenges.
Irrational Thoughts and Behaviors
Lack of sleep can lead to irrational thoughts and behaviors. Sleep deprivation affects our cognitive functioning, making it harder to think rationally and logically. We may find ourselves having distorted thinking patterns or making decisions based on irrational beliefs. These irrational thoughts and behaviors can negatively affect our lives, including personal relationships and decision-making processes.
Heightened Stress Response
Sleep deprivation can intensify our stress response system, making us more susceptible to stress and feeling overwhelmed. When we don’t get enough sleep, our body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol, at higher levels. This can lead to increased anxiety, restlessness, and a heightened stress response. Managing stress becomes even more crucial when sleep deprivation is present.
Poor Coping Skills
Sleep deprivation can impair our ability to cope effectively with stress and challenging situations. When sleep-deprived, our emotional resilience diminishes, making it harder to navigate complex emotions or cope with daily stressors. Finding healthy and adaptive ways to manage stress and maintain our overall well-being can be challenging without sufficient restorative sleep.
Social and Interpersonal Signs of Sleep Deprivation
Difficulty in Communication and Social Interaction
Sleep deprivation can impact our communication skills and social interaction abilities. When sleep-deprived, we may struggle to find the right words, experience difficulty expressing ourselves, or have diminished verbal fluency. This can make conversations challenging and lead to misunderstandings. Additionally, sleep deprivation can decrease our social awareness and make it harder to engage in meaningful and fulfilling interactions with others.
Poor Decision-Making Skills
Sleep deprivation can impair our decision-making skills, affecting our ability to make sound judgments. When we don’t get enough sleep, our cognitive functions become compromised, making it harder to process information, analyze risks, and weigh consequences effectively. This can lead to poor decision-making, both in personal and professional contexts.
Reduced Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
Sleep deprivation can hinder our ability to empathize with others and display emotional intelligence. When we are sleep-deprived, reading and understanding other people’s emotions becomes challenging. This can result in reduced empathy, making it harder to connect with others on an emotional level. Sleep deprivation can also affect our emotional regulation, further impacting our ability to navigate interpersonal relationships.
Strained Relationships or Conflicts
Sleep deprivation can strain our relationships, leading to conflicts and misunderstandings. When we are sleep-deprived, our patience may be tested, and our irritability levels can be heightened. This can create tension within relationships, as our emotional state may impact our interactions with others. It is vital to recognize the impact of sleep deprivation on our relationships and prioritize healthy communication and understanding.
Decreased Work Performance and Teamwork
Sleep deprivation can significantly affect our work performance and ability to collaborate effectively in a team setting. Our concentration, focus, and problem-solving abilities are compromised when we don’t get enough sleep. This can result in decreased productivity and reduced efficiency in completing tasks. Sleep-deprived individuals may struggle to contribute effectively to teamwork, impacting overall work performance.
Physical Health Symptoms Associated with Sleep Deprivation
Weakened Immune System
Sleep deprivation can weaken our immune system, making us more susceptible to illnesses. When we don’t get enough sleep, our immune system’s ability to combat viruses and bacteria becomes compromised. This can increase the likelihood of catching colds, flu, and other infections. Regularly prioritizing adequate rest can help strengthen our immune system and promote overall health.
Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases
Chronic sleep deprivation increases the risk of developing various chronic diseases. Cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and certain cancers have been linked to inadequate sleep. Sleep plays a crucial role in our body’s ability to maintain optimal functioning and repair. Consistently depriving ourselves of sleep can have long-term consequences on our health.
Weight Gain and Obesity
Sleep deprivation can contribute to weight gain and obesity. When we are sleep-deprived, our hormone levels become imbalanced, promoting increased appetite and cravings for high-calorie foods. Moreover, sleep deprivation interferes with our metabolism, making it harder for our bodies to process and utilize carbohydrates effectively. These factors can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of obesity over time.
Cardiovascular Problems
Sleep deprivation can have adverse effects on our cardiovascular health. Lack of sleep has been associated with an increased risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. Sleep plays a vital role in regulating blood pressure and maintaining a healthy heart. Prioritizing quality sleep can help mitigate these risks and promote cardiovascular well-being.
Decreased Libido
Sleep deprivation can hurt our sex drive and overall sexual function. When we are sleep-deprived, our hormone levels can become imbalanced, leading to a decrease in libido. Additionally, fatigue and lack of energy can make it challenging to engage in sexual activities. Adequate rest and prioritizing sleep can help maintain a healthy libido and sexual satisfaction.
Mental and Emotional Health Symptoms Associated with Sleep Deprivation
Increased Risk of Mental Disorders
Sleep deprivation is closely linked to an increased risk of developing mental disorders. Conditions like depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) have been associated with chronic sleep deprivation. Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating our mood and emotional well-being. Prioritizing quality sleep can contribute to maintaining good mental health.
Higher Levels of Stress and Anxiety
Sleep deprivation can significantly contribute to higher levels of stress and anxiety. When we are sleep-deprived, our body’s stress response system is activated more frequently and intensely. This can lead to heightened anxiety, restlessness, and an overall sense of overwhelm. Adequate sleep is essential for managing stress and promoting emotional resilience.
Impaired Emotional Regulation
Lack of sleep can impair our ability to regulate our emotions effectively. When we are sleep-deprived, we may experience difficulty in managing intense or negative emotions. Our emotional responses may become more unpredictable, and we may feel more emotionally reactive. This can impact our relationships and overall well-being. Prioritizing restorative sleep can help support optimal emotional regulation.
Depersonalization and Derealization Experiences
Sleep deprivation can sometimes lead to depersonalization and derealization experiences. These are dissociative symptoms characterized by feeling detached from oneself or the surrounding environment. Sleep deprivation can disrupt our brain’s ability to process sensory information correctly, leading to these unsettling experiences. Adequate sleep and relaxation can help restore a sense of grounding and reduce these symptoms.
Suicidal Thoughts or Tendencies
Severe and prolonged sleep deprivation can increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or tendencies. Sleep deprivation affects our brain chemistry and emotional well-being, making individuals more vulnerable to experiencing depressive episodes and hopelessness. It is crucial to seek professional help if experiencing persistent thoughts of self-harm or suicide and prioritize adequate sleep as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Cognitive Function Symptoms Associated with Sleep Deprivation
Slowed Reaction Times
Sleep deprivation can slow down our reaction times, impairing our ability to respond quickly in various situations. When we are sleep-deprived, our cognitive processing becomes slower, affecting our ability to react promptly to stimuli. Slow reaction times can have significant consequences, especially in situations that require quick decision-making or driving a vehicle.
Impaired Decision-Making and Problem-Solving Abilities
Sleep deprivation can hurt our decision-making and problem-solving abilities. When we don’t get enough sleep, our cognitive functions, such as logical reasoning and critical thinking, become impaired. This can make it challenging to make sound judgments, solve complex problems, and evaluate different options effectively.
Reduced Attention Span and Working Memory
Lack of sleep can lead to a reduced attention span and working memory capacity. When we are sleep-deprived, our ability to sustain focus and concentrate on tasks diminishes. This can result in increased distractibility and difficulty retaining information in our short-term memory. It becomes harder to stay engaged and perform optimally in activities that require sustained attention and memory recall.
Decreased Creativity and Innovation
Sleep deprivation can hinder our creativity and innovative thinking. When we don’t rest enough, our brains may struggle to make new connections and generate fresh ideas. Sleep is vital in consolidating information, enhancing problem-solving skills, and fostering creativity. Prioritizing quality sleep can support our ability to think creatively and develop innovative solutions.
Poor Learning and Academic Performance
Sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on learning and academic performance. When we are sleep-deprived, our ability to concentrate, retain information, and integrate new knowledge is compromised. This can result in difficulty absorbing information during lectures, lower test scores, and reduced academic performance. Prioritizing adequate sleep is crucial for optimizing learning and cognitive functioning.
Behavioral Symptoms Associated with Sleep Deprivation
Increased Risk-Taking Behaviors
Sleep deprivation can contribute to increased risk-taking behaviors. When we are sleep deprived, our ability to evaluate risks and consequences becomes impaired. This can lead to engaging in potentially dangerous or reckless behaviors, such as speeding, substance abuse, or participating in high-risk activities without proper precautions.
Impulsive Actions and Poor Judgment
The lack of sleep can make us more prone to impulsive actions and poor judgment. Sleep deprivation affects our cognitive processes, including the ability to reason and weigh the potential outcomes of our actions. We may make impulsive decisions without considering the long-term consequences, which can negatively affect various aspects of our lives.
Decreased Motivation and Productivity
Sleep deprivation can significantly decrease our motivation and hinder our productivity. When we are sleep-deprived, we may feel constantly tired, drained, and lacking the drive to accomplish tasks. This can lead to decreased productivity and reduced efficiency in completing everyday responsibilities. Prioritizing quality sleep is essential for maintaining high motivation levels and optimal productivity.
Sleep-Related Accidents
One of the behavioral symptoms associated with sleep deprivation is an increased risk of sleep-related accidents. When we are sleep-deprived, our reaction times, attention span, and overall cognitive functioning are impaired. This can make us more prone to accidents, such as car crashes, workplace injuries, or falls, due to reduced alertness and impaired judgment.
Social Isolation and Withdrawal
Sleep deprivation can contribute to social isolation and withdrawal tendencies. Sleep deprivation affects our overall well-being and mood, making us less likely to engage in social activities and connect with others. Sleep deprivation can lead to irritability, low energy, and reduced interest in social interactions, resulting in withdrawing from social engagements and isolating ourselves.
Long-term Effects of Sleep Deprivation
Increased Risk of Chronic Health Conditions
Consistently experiencing sleep deprivation can have severe long-term consequences on our health. Chronic sleep deprivation increases the risk of developing various chronic health conditions. These may include cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, weakened immune system, and certain cancers. Prioritizing quality sleep is essential to mitigate these risks and promote overall health and well-being.
Impaired Cognitive Function and Memory Decline
Long-term sleep deprivation can have a detrimental effect on cognitive function and memory. Chronic lack of sleep is associated with declining cognitive abilities, including memory recall, attention span, and problem-solving skills. Over time, these cognitive impairments can become more pronounced, affecting our overall cognitive health and quality of life.
Negative Impact on Mental Health and Emotional Well-being
Prolonged sleep deprivation can negatively impact mental health and emotional well-being. Chronic lack of sleep increases the risk of developing mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and mood disorders. Sleep deprivation can exacerbate mental health issues and contribute to emotional instability and low resilience to stress.
Reduced Quality of Life and Life Expectancy
Sleep deprivation can significantly reduce our quality of life and potentially impact our life expectancy. Lack of adequate sleep can lead to decreased energy levels, impaired cognitive functioning, reduced emotional well-being, and decreased overall functioning. Prioritizing quality sleep is crucial for maintaining a high quality of life and promoting longevity.
Decreased Productivity and Performance in All Areas of Life
Chronic sleep deprivation can broadly affect our productivity and performance in all areas of life. Our cognitive abilities, decision-making skills, and overall performance diminish when we consistently lack sleep. This can affect our work or academic performance, personal relationships, and ability to engage in activities that bring us joy and fulfillment.
How to Recognize Sleep Deprivation in Yourself and Others
Keep Track of Your Sleep Patterns and Quality
One of the most effective ways to recognize sleep deprivation is by keeping track of your sleep patterns and quality. Pay attention to the number of hours you sleep each night and how rested you feel upon waking up. Keeping a sleep journal or using a sleep-tracking app can help you identify insufficient sleep patterns or poor sleep quality.
Monitor Changes in Mood and Behavior
Be mindful of changes in your mood and behavior that may indicate sleep deprivation. If you feel consistently irritable, moody, or experiencing heightened stress levels, it may be a sign that you are not getting enough quality sleep. It is essential to assess whether these changes coincide with insufficient rest periods.
Seek Feedback from Others
If you are unsure whether you are experiencing sleep deprivation, seek feedback from trusted individuals. They may notice changes in your behavior, cognitive functioning, or overall well-being that you may not recognize. Don’t hesitate to ask for their observations and insights to better understand the impact of sleep deprivation on your daily life.
Pay Attention to Physical and Mental Health Symptoms
Be attentive to any physical or mental health symptoms attributed to sleep deprivation. These symptoms may include frequent headaches, muscle pain, difficulties with concentration and memory, increased anxiety, or a weakened immune system. Connecting these symptoms with your sleep patterns can help identify potential sleep deprivation.
Consider Consulting a Sleep Specialist
If you suspect that you or someone you know may be experiencing sleep deprivation, it is advisable to consult a sleep specialist.
Sleep specialists are trained professionals who can assess your sleep patterns, identify any underlying sleep disorders, and provide recommendations for improving your sleep quality. Seeking professional help can be instrumental in addressing sleep deprivation effectively.
In conclusion, sleep deprivation can manifest through various physical, behavioral, emotional, and social symptoms that can significantly impact our overall well-being. Recognizing the signs of sleep deprivation in ourselves and others is essential to take appropriate measures to prioritize restorative sleep.
By understanding the comprehensive effects of sleep deprivation, we can make informed decisions to promote our physical and mental health, enhance our cognitive functioning, and improve our quality of life. Remember, a good night’s sleep is not just a luxury but a fundamental necessity for our overall well-being and vitality.